
Low Frequency Inverters
Dec 10, 2019 · we have mostly seen high frequency in the grid tie sector and inverters from China, right now the primary us one I am seeing is the solark which is getting some pretty good

Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: Technical
Jul 17, 2025 · This analysis evaluates the performance characteristics of low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverters based on current industry data and technical literature. Key

Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and
Jun 13, 2025 · High frequency inverters work well when you want efficiency, compact size, and lower cost. Low frequency inverters offer better surge capacity, power quality, and reliability for

Hybrid Inverters With Low Frequency: Merging Efficiency
May 31, 2024 · This technological breakthrough has merged the best qualities of high-frequency and low- frequency inverter s, providing a perfect blend of efficiency and reliability. 2.
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · If you are looking for an inverter for fixed power stations, precision instruments, or other related fields, then go with power-frequency inverters. However, a high-frequency

High Frequency vs. Low Frequency Inverter
Jul 29, 2022 · A lot of the most popular AIO inverters are High Frequency Transformerless. How important is it to use the correct family of transformer (high vs. low freq) for to power devices

What''s the difference between a high frequency and Low frequency inverter?
The IGBT high frequency rectifier, which is used in the high frequency inverter, has a high switching rate. However, it has a tight voltage and current area during operation and has low

Inverters High or Low Frequency ? | DIY Solar Power Forum
Apr 15, 2020 · Low-frequency inverters use high-speed switches to invert (or change) the DC to AC, but drive these switches at the same frequency as the AC sine wave which is 60 Hz (60
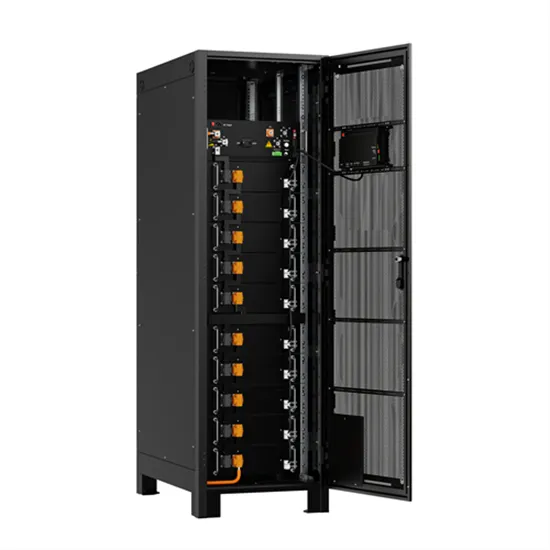

High-frequency versus low-frequency inverters which is right
Jun 13, 2025 · Compare high-frequency and low-frequency frequency inverters to find the best fit for your power needs, efficiency, surge capacity, and reliability.
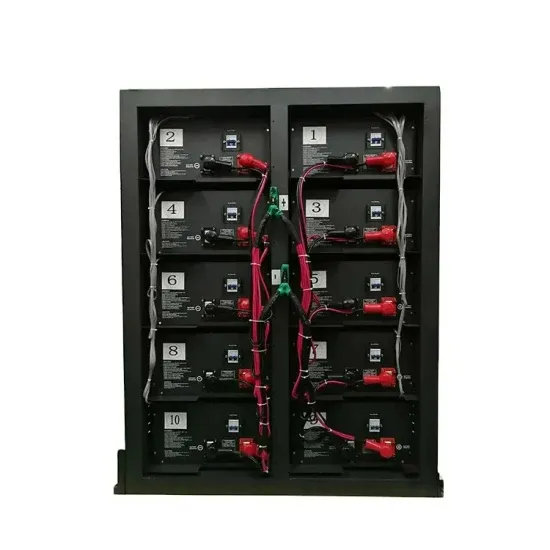

Which is Better: Low Frequency or High Frequency Inverter?
Mar 20, 2025 · High-Frequency Inverters: High-frequency inverters are generally more efficient, especially in systems that require smaller power outputs. They operate with less power loss

Low vs High frequency inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
Jun 13, 2022 · The 6kxp has been very robust so far. I can recall my first month or so on this forum feeling a similar sentiment or opinion. That I just wanted/needed a low frequency and

Demystifying High Frequency vs Low Frequency
Jul 2, 2023 · The best type of inverter for a particular application will depend on the specific requirement of that application. For example, a High-frequency

Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Jul 25, 2025 · Yet, not all inverters are created equal. One of the most critical architectural decisions an engineer faces is the choice between a line-frequency (or low-frequency) and a

High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter: How to
Aug 18, 2025 · High frequency inverters and low frequency inverters are two common types of inverters with distinct differences in their application, operating principles, and characteristics:

Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Aug 15, 2025 · Explore the key differences in low frequency vs high frequency inverters including their applications, advantages, and which is best for your

6 FAQs about [Inverter has good high frequency and good low frequency]
What is the difference between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters?
When it comes to power conversion, charging, and handling loads, high-frequency inverters often provide better efficiency due to their advanced switching techniques. However, low-frequency inverters are favored for applications requiring high power surge capabilities. The high-frequency inverter board is a marvel of modern engineering.
Should you choose a low frequency or high frequency inverter?
For applications that require high power quality and are sensitive to the electromagnetic environment, you can choose an Low Frequency inverter; while for applications that require portability, high efficiency and fast response, High frequency inverters are more advantageous.
What is the difference between high frequency and industrial frequency inverter?
The same power inverter industrial frequency inverter is far heavier than the high-frequency inverter, high frequency inverter is small in size, light in weight, high in efficiency, low no-load load, but can’t be connected to a full inductive load, and overload capacity is poor.
What are the advantages of a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverters typically have an output of 20kHz or higher. Smaller size and weight compared to low-frequency inverters. Higher efficiency due to reduced power losses. Greater accuracy in output waveform due to the high frequency. Lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to higher switching frequency.
What are high-frequency inverters used for?
High-frequency inverters are versatile and are used in a wide range of applications. They are particularly popular in solar power systems, where efficiency and compact design are crucial. Additionally, they are found in: Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) for quick response times during power outages.
What is a low frequency solar inverter?
The low frequency solar inverter firstly turns the DC into IF low-voltage AC, and then boosts it into 220V, 50Hz AC for the load through the IF transformer. High frequency inverters and low frequency inverters are two common types of inverters with distinct differences in their application, operating principles, and characteristics:
Update Information
- Which is better high frequency or low frequency inverter
- High voltage and low current inverter
- Photovoltaic inverter low frequency tolerance setting
- Is a pure wave inverter a high frequency
- Rack-mounted inverter high frequency
- 24V1000W high frequency inverter production
- Korean high frequency inverter installation
- Inverter high frequency arm waveform
- High frequency inverter field
- Tripoli high frequency inverter price
- High frequency inverter produces sine wave
- Construction site low voltage to high voltage inverter
- Inverter Type High Frequency Power Frequency
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
