
High-frequency versus low-frequency inverters which is right
Jun 13, 2025 · Key Takeaways High-frequency inverters are small, efficient, and cost-effective, making them ideal for light loads and limited spaces like homes and offices. Low-frequency
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
Dec 17, 2024 · 2. Low Frequency Inverters: Robust and Durable: Low frequency inverters are better suited for applications requiring high power output and reliability. Their robust design
Which Is Better Low Frequency or High-Frequency Inverter
Feb 23, 2024 · The document compares low frequency inverters, which operate near power line frequencies, to high frequency inverters, which use much higher switching frequencies. Low

Which is better low-frequency or high-frequency inverter?
Apr 2, 2020 · Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability. Low-frequency inverters are designed to deal with

Which is Better: Low Frequency or High Frequency Inverter?
Mar 20, 2025 · When it comes to choosing an inverter for your home or business, one of the most important decisions you will make is whether to go with a low-frequency or high-frequency

High Frequency vs. Low Frequency Inverter
Jul 29, 2022 · A lot of the most popular AIO inverters are High Frequency Transformerless. How important is it to use the correct family of transformer (high vs. low freq) for to power devices

High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the

Comparing High Frequency UPS and Low Frequency UPS
Mar 27, 2025 · Low-Frequency Inverters vs. High-Frequency Inverters A low-frequency inverter relies on transformer-based conversion, using a heavy-duty transformer to convert DC power

Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Understanding the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters is vital for anyone involved in renewable energy or considering an uninterrupted power supply (UPS)

Inverters High or Low Frequency ? | DIY Solar Power Forum
Apr 15, 2020 · Low-frequency inverters use high-speed switches to invert (or change) the DC to AC, but drive these switches at the same frequency as the AC sine wave which is 60 Hz (60

Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · Low-frequency power inverters have much better peak power capability to manage large loads with power spikes than high-frequency inverters. In fact, low-frequency inverters

High frequency verses low frequency inverters
Nov 26, 2022 · What is the difference between high, or low frequency inverters the pros and cons? I have seen a few posts someone said low was better for high surge load like AC units,

Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Aug 15, 2025 · Explore the key differences in low frequency vs high frequency inverters including their applications, advantages, and which is best for your

High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
High-Frequency Inverters: High-frequency inverters can handle moderate surges, but their surge capacity is generally lower than low-frequency inverters. They may struggle to run devices with

High frequency versus low inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
Nov 18, 2019 · Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency | Magnum Dimensions Understand the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters

Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and
High frequency inverters are compact and efficient, making them ideal for applications where space is limited, such as solar power systems and portable devices. Low frequency inverters

6 FAQs about [Which is better high frequency or low frequency inverter ]
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and other components, leading to lower power losses. Low-frequency inverters have lower efficiency due to higher losses in magnetic components and switching devices.
What are the advantages of a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverters typically have an output of 20kHz or higher. Smaller size and weight compared to low-frequency inverters. Higher efficiency due to reduced power losses. Greater accuracy in output waveform due to the high frequency. Lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to higher switching frequency.
How do I choose a low frequency or high frequency inverter?
When deciding between a low frequency or high frequency inverter, it is important to consider the power requirements of the appliances and devices that you wish to power. Heavy-duty items, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, may require a low frequency inverter with high surge capacity.
Are low frequency inverters reliable?
These transformers operate at lower frequencies (typically 50 or 60 Hz), making them robust and highly reliable. Low-frequency inverters are known for their durability and ability to handle high surge loads.
What are the advantages of a low frequency inverter?
Simplicity, ruggedness, low EMI, and low acoustic noise are some of the advantages of low frequency inverters. They also have higher overload capacity. What semiconductor devices are commonly used in high frequency inverters?
What is a low frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverters are known for their durability and ability to handle high surge loads. The heavy transformers inside these inverters allow them to deliver much power for short bursts, which is essential for starting devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, or power tools that need extra energy to start running.
Update Information
- Which brand should I choose for high frequency inverter
- Inverter has good high frequency and good low frequency
- Tripoli high frequency inverter price
- High frequency inverter brand
- Which is better inverter or photovoltaic
- Sri Lanka High Frequency Power Inverter
- NFA inverter is a high frequency machine
- Which is better UPS or battery inverter
- Benefits of high frequency inverter
- North Africa High Frequency Inverter Brand Ranking
- Symmetrical front stage of high frequency inverter
- 800w high frequency inverter
- Czech high frequency inverter structure
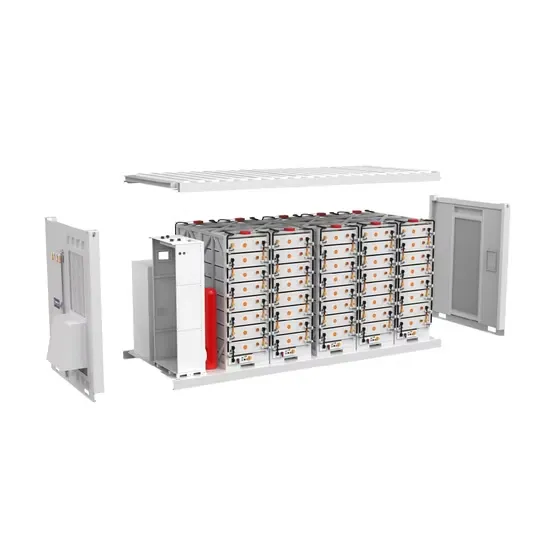
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
