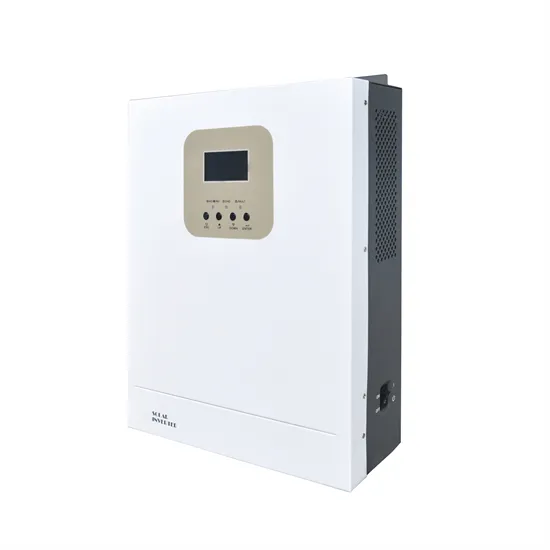

High frequency verses low frequency inverters
Nov 26, 2022 · What is the difference between high, or low frequency inverters the pros and cons? I have seen a few posts someone said low was better for high surge load like AC units,

Frequency inverter design
Sep 5, 2018 · Gozuk inverters are suitable in the fields of power, iron and steel, HVAC, oil, mine, construction, etc for the high-voltage motor''s speed adjustment, energy saving, soft starting

How to Distinguish High Frequency Inverter and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 11, 2024 · Low frequency inverters produce less electromagnetic interference, but can only produce lower AC power frequencies, while high frequency inverters can produce higher

Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · If you are looking for an inverter for fixed power stations, precision instruments, or other related fields, then go with power-frequency inverters. However, a high-frequency

Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and
Oct 26, 2024 · Understanding the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters is vital for anyone involved in renewable energy or considering an uninterrupted

Power Frequency Inverters for High Voltage Tests
Oct 22, 2007 · Two level voltage source inverters with connected resonant or filter circuits are normally used to generate a high-quality test voltage by feedback control. The properties of

High-Frequency Inverters: From Photovoltaic, Wind, and
Jul 26, 2022 · (3) efficiency, and (4) power density. Conventional approach to inverter design is typically based on the architecture illustrated in Fig. 29.1a. A problematic feature of such an
Design and Development of High Frequency Inverter for
In this paper, Simulation & Hardware development of High frequency Inverter with 90KHz frequency with Pulse Width Modulation switching strategy is presented. The inverter topology

Inverter Low Frequency vs High Frequency | How Do I
Mar 31, 2024 · There are two main types of inverters: low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters. Low-frequency inverters operate at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, which is the same

Inverter design using high frequency
Feb 27, 2021 · ABSTRACT In this paper we are developing inverter which is very cheap in cost and portable we are using 50KHz frequency for DC Technique and output 250V DC, 500mA,

How to Distinguish High Frequency Inverter and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 11, 2024 · Inverters come in many different shapes and sizes. There are two main contrasting characteristics between different types of inverters: The type of power output, categorized by

High Frequency Power Inverters: A Guide To Modern Solutions
May 4, 2024 · High frequency power inverters have revolutionized the field of electrical conversion, enabling efficient and reliable power supply solutions for various applications. In

A review on topology and control strategies of high-power inverters
Feb 15, 2025 · A comprehensive analysis of high-power multilevel inverter topologies within solar PV systems is presented herein. Subsequently, an exhaustive examination of the control

Review of very high frequency power converters
Jul 1, 2020 · The matching networks are added between the inverter stages and rectifier stages to adjust the equivalent impedance of the rectifier stage. Fig. 4

Single-Stage Multi-Input Buck Type High-Frequency Link''s Inverters
Jan 1, 2022 · A class of single-stage multi-input Buck type high-frequency link''s inverters with series and simultaneous power supply are proposed in this article, and the key technologies

Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
4 days ago · There are two distinct types of industrial grade power inverters distinguished by the size of their transformers, and the switching speed of their transistors. The ability of an inverter
Design a High Frequency Power Inverter Using Ferrite-Core
Jan 22, 2024 · To minimize the corrosion of electrodes in ohmic heating a variable high frequency power source instead of commercial frequency (50/60 Hz) is being proposed here. This

Low Frequency Versus High Frequency PWM in Medium Voltage, High Power
Sep 12, 2024 · One of the main advantages of multi-level inverters (MLI) is their ability to achieve high power quality and high efficiency power conversion. With the emergence of wide-band

A high-frequency current-output-type inverter aimed for wireless power
Sep 24, 2015 · Wireless power transmission (WPT) using magnetic resonance has been attracting increasing attention from power electronics engineers and industry. A number of studies have

6 FAQs about [Inverter Type High Frequency Power Frequency]
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
Here is the major difference of them: Thanks to the heavy-duty transformer, low frequency inverters have much higher peak power capacity and reliability. The transformer handles higher power spikes with longer duration than high-frequency inverters when it comes to driving inductive loads such as electric motor, pump, compressor, air conditioners.
What is a high frequency inverter?
The high frequency inverter can deliver the same power at higher frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer, as a result, the HF inverter is often called transformer-less inverter, or TL inverter.
What are common high-frequency inverter circuit configurations?
Common high-frequency inverter circuit configurations include: Key design factors for high-frequency inverters: Switching frequency – Higher frequency allows smaller filter components but increases losses. Optimize based on tradeoffs. Filter components – Smaller inductors and capacitors possible at high frequencies. Balance size versus performance.
How do I choose a low frequency or high frequency inverter?
When deciding between a low frequency or high frequency inverter, it is important to consider the power requirements of the appliances and devices that you wish to power. Heavy-duty items, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, may require a low frequency inverter with high surge capacity.
What are the advantages of a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverters typically have an output of 20kHz or higher. Smaller size and weight compared to low-frequency inverters. Higher efficiency due to reduced power losses. Greater accuracy in output waveform due to the high frequency. Lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to higher switching frequency.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Both of the two type of inverters can be built with utility charger or solar charger and be called “inverter charger”. Here is the major difference of them: Thanks to the heavy-duty transformer, low frequency inverters have much higher peak power capacity and reliability.
Update Information
- High frequency inverter power supply
- Austria high frequency power inverter
- Sea Island 2025 Type A High Frequency Inverter
- Simple high power inverter
- How to connect the high frequency power supply of the base station
- High power inverter
- EK high power inverter
- Czech high frequency inverter structure
- 24V1000W high frequency inverter production
- High voltage power supply full bridge inverter price
- High frequency inverter converted to water cooling
- Wellington power frequency inverter price
- Inverter power reduction and frequency reduction for grid connection
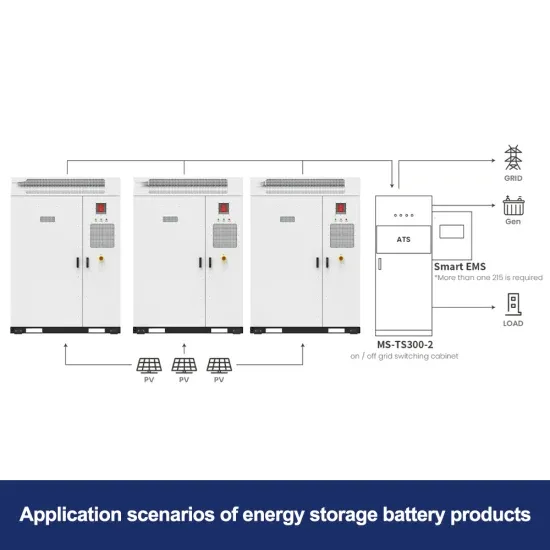
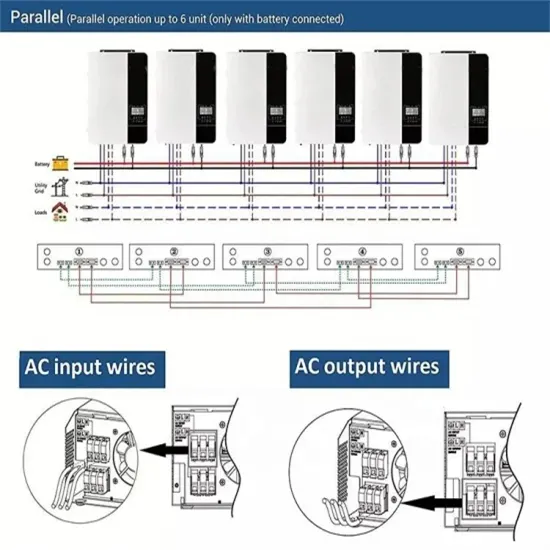
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
