
The difference between voltage type and current type inverter
Sep 12, 2024 · For voltage type inverters, the output voltage can be filtered through a large capacitor. Because the capacitance is relatively large, electrolytic capacitors are generally used.

What is voltage type and current type inverter, and what are
3, the difference between the dynamic response; dynamic response when speed control current-type inverter DC voltage Ua can quickly change the size and direction, so the dynamic

What is voltage type and current type inverter, and what are
What is voltage type and current type inverter? Voltage inverter is an inverter that converts DC from a voltage source to AC, and the DC circuit is filtered by a capacitor; Current type inverter

CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width modulation, or PWM. The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power

Paper Title (use style: paper title)
Mar 13, 2025 · The inverter in this scheme works as a step-up converter. By controlling the amplitude and phase of the machine winding current, it maintains a set voltage Vdc in the DC

What Is the Difference Between Mppt And Pwm Inverter?
Jun 21, 2025 · PWM inverters have a simple structure, mature technology, and a low price. They are suitable for small solar energy scenarios with limited budgets and low efficiency

VSI vs. CSI: Voltage Source Inverter vs. Current Source Inverter
Explore the differences between Voltage Source Inverters (VSI) and Current Source Inverters (CSI), their characteristics, and applications in power electronics for DC to AC conversion.

Microsoft Word
Oct 24, 2023 · Voltage and current controlled inverters look quite different on a sub 20ms time scale. On a longer time scale (ie seconds) however, inverters used for injection of energy from

Current source inverter vs. voltage source inverter
Aug 25, 2024 · Abstract In the medium voltage adjustable speed drive market, the various topologies have evolved with components, design, and reliability. The two major types of

Choosing the Right 3-Level Inverter: T-Type vs. T-NPC
Jun 19, 2025 · The fundamental difference between the T-type and T-NPC lies in how they connect the output to the neutral point. This structural difference is the root of their varying

Solar Charge Controllers Explained – MPPT vs
Jun 19, 2025 · Learn everything about solar controllers (MPPT & PWM), how they work, how to size them, and how to wire them with batteries, solar panels, and

Key Differences Between Current-Type and Voltage-Type VFDs
A current-type VFD, known as a Current Source Inverter, adjusts motor speed by managing current. In contrast, a voltage-type VFD, or Voltage Source Inverter, modifies speed by varying

Power Tips: Voltage mode or current mode?
Jul 27, 2023 · There are two types of fixed-frequency pulse-width modulation (PWM) control: voltage mode (VM) and current mode (CM). Figure 1 shows a diagram that explains both

What is voltage type and current type inverter, and what are
What is the difference between voltage type and current type, for voltage type inverter, the output voltage can be filtered by large capacity capacitor . The structure of the rectifier is exactly the

Difference between Sine Wave and Square Wave
Feb 8, 2021 · By inputting control signals at points A, B, C, and D, the on and off of the MOS tube can be controlled, thus current Direction of the load can be

Current source inverter vs. voltage source inverter
Aug 25, 2024 · The two major types of drives are known as voltage source inverter (VSI) and current source inverter (CSI). In industrial markets, the VSI design has proven to be more
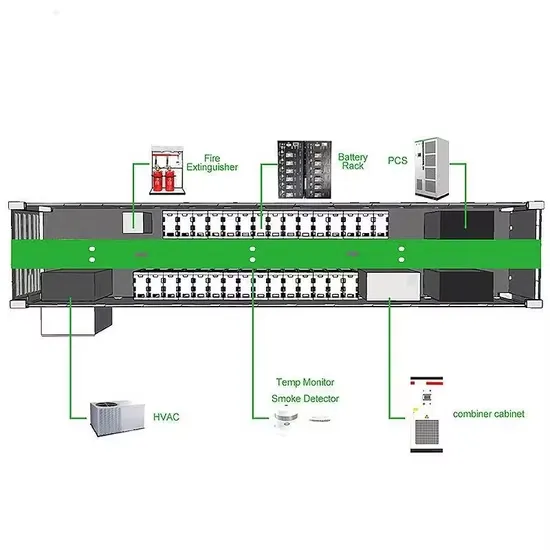
Introduction to voltage type inverter and current type inverter
According to the working mode of the main circuit, they can be divided into voltage type inverters and current type inverters; according to the switching mode, they can be divided into PAM

Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Drives
Jun 14, 2016 · Power Conversion Unit The block diagram below shows the power conversion unit in Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) drives. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier provides

6 FAQs about [Difference between voltage type and current type PWM inverter]
Are voltage source type inverters easier to control?
Voltage source type inverters are easier to control than current source type inverters. It is easier to obtain a regulated voltage than a regulated current, and voltage source type inverters can directly adjust the voltage applied to a load by varying the conduction ratio (i.e., the pulse width of a PWM signal).
What is a current source type inverter?
Current source type inverters control the output current. A large-value inductor is placed on the input DC line of the inverter in series. And the inverter acts as a current source. The inverter output needs to have characteristics of a voltage source.
What are voltage and current controlled inverters?
Voltage and current controlled inverters look quite different on a sub 20ms time scale. On a longer time scale (ie seconds) however, inverters used for injection of energy from a PV array directly into the grid are controlled as power sources ie. they inject “constant” power into the grid at close to unity power factor.
What is the difference between current source and voltage source inverter?
What Is The Difference between Current Source Inverter and Voltage Source Inverter? . In the field of power electronics, Current Source Inverters (CSIs) and Voltage Source Inverters (VSIs) are two fundamental types of inverters used to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
What are the different types of PWM inverters?
Table 2.1 provides an overview of inverter categories. Voltage-type PWM inverters are most commonly used. These inverters are further divided into two categories, depending on the commutation method used: 120° commutation primarily used for small motor applications and 180° commutation used for many motor and power supply applications.
What are the different types of inverters?
The two primary types of inverters—Voltage Source Inverters (VSIs) and Current Source Inverters (CSIs)—differ in their approach to this conversion process. Selecting the right inverter type depends on factors such as the nature of the power source, desired control precision, application requirements, and system complexity. What is Inverter?
Update Information
- Three-phase voltage type pwm inverter design
- Voltage type inverter classification
- What is a voltage tracking PWM inverter
- Inverter outputs high current and high voltage
- Does the inverter have high voltage and high current
- Voltage outer loop current inner loop lcl inverter
- Pwm voltage inverter
- High voltage and large capacity inverter
- Can the inverter convert high voltage into low voltage
- Can the inverter change to high voltage
- Igbt full bridge inverter output voltage
- Solar voltage regulation and stabilization inverter
- Bangladesh voltage stabilizer inverter price
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
