
DC-AC Inverter Circuit
Feb 28, 2025 · Inverter and motor controller are two different components in a motor drive system that differ in their functions and applications. 1. Function: The inverter is mainly responsible for

Understanding the Distinction Between AC Drives and Inverters
Posted on 26th Mar 2024 Understanding the Distinction Between AC Drives and Inverters: Clarifying Key Differences In the realm of electrical engineering and industrial automation, the

Basics of inverter control and application to motor control
Jul 8, 2025 · The inverter allows altering the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to an electric motor, which governs the motor''s speed and torque. Inverter control is essentially the

What are Inverters and AC Input Brushless DC Motors?
4 days ago · Inverters are used in combination with a three-phase 200 VAC motors to control the rotation speed by changing the power supply frequency. All you need to connect is a power

AC Motor Inverter Design: Strategies For Efficient Speed
Apr 14, 2025 · What Is AC Motor Inverter Design and Why Is It Important for Speed Control? AC motor inverter design refers to the engineering and technology involved in creating devices

Guide to Frequency Inverters: Optimizing Motor
Nov 13, 2024 · I. Introduction to Frequency Inverters (VFDs) Frequency inverters, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), are essential components in

AC Motor Inverter: How It Works, Its Functionality, And Key
May 20, 2025 · AC motor inverters allow for precise speed control and energy savings. They operate by adjusting the input frequency to the motor, which directly influences its speed.

Inverter Duty vs Conventional AC Induction Motors
Dec 6, 2010 · Good Answer: Here s part of an article you might use in your report How to choose a general purpose motor vs. an inverter duty motor General purpose motors have been around
The difference between an inverter and a motor controller
Feb 28, 2025 · The role of the motor inverter The motor inverter is an electric energy conversion device that converts DC power into AC power to control the speed and torque of the AC motor.

Running A Small AC Motor From An Inverter: The Power Of
Jun 19, 2025 · Small AC motors usually run on a 230/400V, 50Hz supply. You can use an inverter drive to power them at 400V and 87Hz. Delta connection is common for these motors. This

Introduction to AC Motor Inverter
Dec 15, 2020 · The AC motor inverter is first converted to DC power through an oscillating circuit, and then the DC power is switched to AC power by electronic components. Generally, a more

AC Motor Inverter Duty: Superior Speed Control For High
Apr 14, 2025 · An inverter-duty motor is a type of AC motor made for Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). It can manage voltage spikes from VFDs, especially over long cable lengths. These

What Is an Inverter in an Electric Vehicle?
Aug 9, 2023 · An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC), which is supplied from a battery, into alternating current (AC). A motor in an electric vehicle runs on this alternating

Variable Frequency Inverter and Motor Matching Guide
Dec 21, 2023 · Common motor types include induction motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors, etc. Each type has its own unique operating principles and characteristics and

AC Motor vs Inverter Generator: Pros, Cons, and Which is
Apr 17, 2025 · An AC motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, while an inverter generator produces electricity through an engine and inverter technology, allowing for variable

Analysis of the difference between inverter motor and ordinary motor
Apr 24, 2024 · It controls the speed and power of the motor by changing the frequency of the power supply. Inverter motors usually consist of inverters, motors, and control systems. The

Electric Motor Inverter Explained
Jun 23, 2025 · EV inverters do more than drive the motor — they also enable regenerative braking by reversing the power flow: Instead of pushing current to the motor, the inverter

8 Project Planning for AC Motors with Inverter
Aug 1, 2014 · SEW-EURODRIVE offers the following inverter series: MOVITRAC® B: Compact and inexpensive frequency inverter for the power range 0.3-175HP. Single-phase and three

Understanding the Distinction Between AC Drives and Inverters
Mar 26, 2024 · While AC drives are a type of inverter, not all inverters serve the function of motor speed control. In the context of motor control, inverters typically refer to devices that convert

Inverters: Boosting AC Motor Performance for Enhanced
Jun 3, 2025 · An inverter for an AC motor converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). It controls the motor''s speed and torque by adjusting the power frequency. This device

6 FAQs about [Inverter and AC Motor]
What is AC motor inverter?
AC motor inverters are devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to control the speed and torque of electric motors. They are essential for improving energy efficiency in various applications, such as fans, pumps, and conveyor systems. 1. Functionality 2. Types 3. Applications 4. Benefits 5. Considerations
What is an inverter drive?
Inverter drives are essential for applications requiring variable speed motors, such as industrial automation and HVAC systems. They convert fixed frequency AC power from the mains into adjustable frequency and voltage output, enabling efficient operation and energy savings. Inverter drives serve multiple purposes in various industrial settings.
How do AC drives (inverters) work?
The higher the frequency value, the faster the motor will rotate, and the lower the frequency value, the slower motor will rotate. The AC Drive (inverter) enables variable speed operation by changing the frequency. By the way, what did the AC Drives (inverters) effect to generate a wide range of frequencies from the rated commercial power supply?
How does AC drive (inverter) change motor speed?
To change the motor speed, that is the number of revolutions, AC Drive (inverter) makes the frequency (Hz) to motors change. The higher the frequency value, the faster the motor will rotate, and the lower the frequency value, the slower motor will rotate. The AC Drive (inverter) enables variable speed operation by changing the frequency.
How to control AC drive (inverter)?
Standard control methods for general-purpose AC Drives (inverters) are split with V/f control and vector control. V/f control is to stabilize the ratio of the voltage (V) and frequency (f) from an AC Drive (inverter). For example, in case of an AC Drive (inverter) with 200V power supply voltage, it outputs 200V at 60Hz and 100V at 30Hz.
How do inverters control motor speed?
Frequency control: Inverters adjust the frequency of the output AC signal, which directly controls the speed of the motor. The principle of frequency-to-speed relationship indicates that increasing frequency increases motor speed.
Update Information
- AC inverter 12v to 220v 5KW
- 3kw inverter with induction motor
- DC AC boost inverter price
- Inverter power AC voltage
- Inverter that can increase motor power
- Differences between AC inverter and DC inverter
- Inverter 48v with 400v motor
- Fully automatic emergency AC DC inverter
- 220v AC to 12v DC connected to inverter
- DC AC inverter bridge
- London three-phase motor inverter model
- DC to AC inverter design
- Inverter connected to motor power
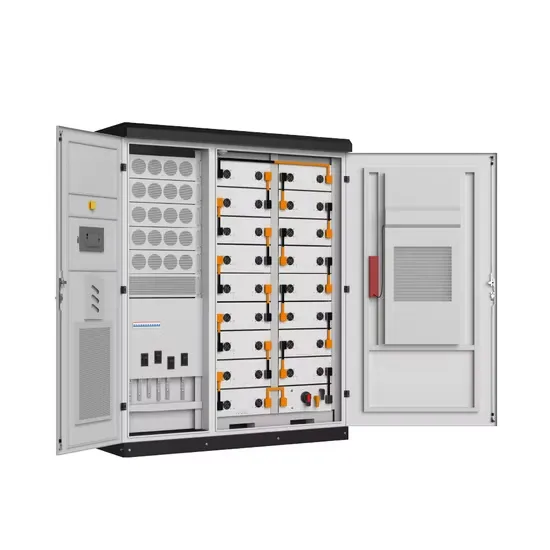
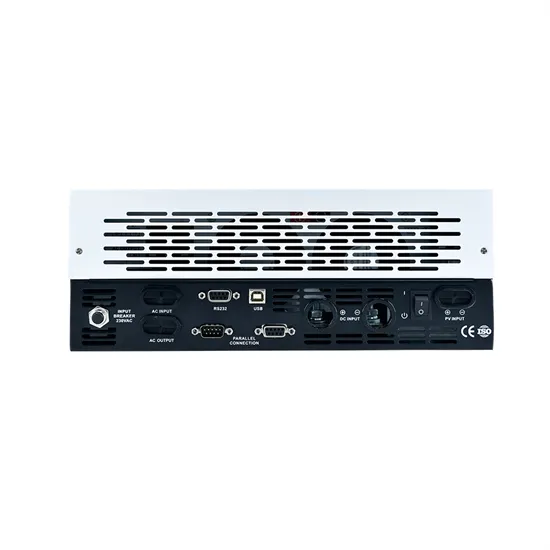
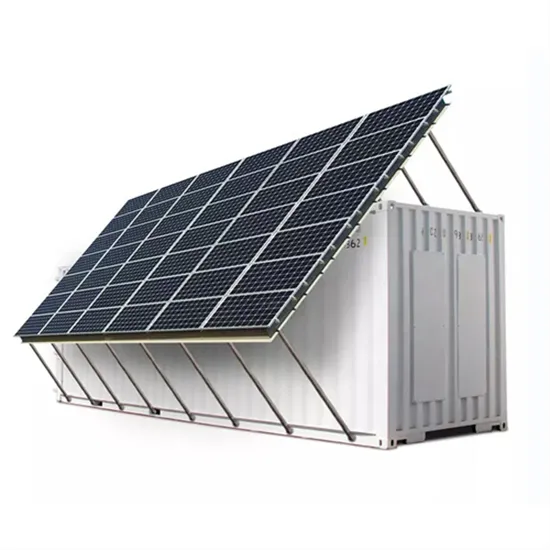
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
