Inverter vs Rectifier Efficiency: What to Know About Power
Nov 4, 2024 · Both inverters and rectifiers serve unique functions, but they play an essential role in ensuring our power systems run efficiently. In this guide, we''ll break down what these

full bridge rectifier into an inverter | All About Circuits
Dec 20, 2020 · As for rectifying AC into DC - you''ll (likely) need a full wave bridge rectifier. Now, for how you''re controlling that final voltage - that in itself can present other problems.

Rectifiers vs. Inverters in Electric Vehicles: A Technical
Oct 28, 2024 · The motion of the vehicle spins the motor, producing AC power. This power is then converted back into DC power by the rectifier, allowing it to be stored in the battery for later

Design of a Single Phase HERIC-SPWM
Apr 16, 2022 · Figure 1. Overall System the source uses a source of 220V PLN nets then rectified to a DC voltage using an uncontrolled full-bridge rectifier before being channeled to the current

The difference between rectifier and inverter
Mar 26, 2025 · Rectifier: In communication systems, rectifiers convert AC power into DC power and supply power to communication equipment. Inverter: In a solar power generation system,

Inverters and Rectifiers: How to Convert DC to
Jun 29, 2025 · 1What are inverters and rectifiers? Inverters and rectifiers are electronic circuits that can change the type of electric current. An inverter

Energy efficiency enhancement in full-bridge PV inverters
Jan 1, 2021 · Nowadays, the fast development of wide-bandgap (WBG) devices brings new challenges to transformerless inverters, e.g., electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues, but

Analysis of a ZVDS Class-DE current-driven full
Feb 1, 2025 · The accurate, systematic, and effective design method of compensation network capacitance based on the series-series resonant topology is presented for reducing the

Full Bridge Resonant Inverter for Blade Induction Heating
Jan 1, 2019 · This paper presents blade induction heating application using full bridge resonant inverter including six parts: step-down transformer, full wave bridge rectifier, Pulse Width

A 5-Level HERIC Active-Clamped Inverter With Full Reactive Power
May 3, 2023 · Distributed generation systems integrated into the modern electrical grid demand novel circuit architectures that can combine high efficiency and high power density together.

The difference between rectifier and inverter
Mar 26, 2025 · Rectifier converts AC to DC, and inverter converts DC to AC Rectifier and inverter are two important devices in the field of power electronics. Their functions, working principles

Choosing the right DC/DC converter for your energy storage
Sep 30, 2020 · Features Digitally-controlled bi-directional power stage operating as half-bridge battery charger and current fed full-bridge boost converter 2kW rated operation for discharge

Comparison of PIM modules with separate inverter and
Oct 24, 2024 · Their circuit topology diagram is the rectifier bridge plus three-phase inverter circuit. Here we take the frequency converter as an example. Generally speaking, the motor

Active Rectifiers and Source‐side Inverters
Nov 28, 2023 · Both active rectifiers and source‐side inverters have their three‐phase AC side connected to the AC source. The chapter discusses the design of the power stage of the

Inverter and Rectifier Maintenance: What You Need to Know
Oct 23, 2024 · In our increasingly electrified world, inverters and rectifiers play a crucial role in converting electrical energy. Whether you''re managing a solar power system, a UPS, or

Difference Between An Inverter & A Rectifier
Jul 17, 2017 · Rectifiers come in two basic types: half-wave and full-wave. A half-wave rectifier allows electricity of only one polarity (positive or negative) to

Inverter/rectifier technologies | Wireless Power Transfer
Aug 6, 2024 · This chapter introduces a design theory for optimal magnetic-coupling wireless power transfer (WPT) systems from a circuit-theory viewpoint. WPT systems are generally

Lecture Notes on Power Electronics
Mar 14, 2025 · Single-phase Half and Full bridge Inverter, Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) technique for voltage control, SPWM Technique 1-phase inverters, Auxiliary Commutated (Mc

What Is the Difference Between Transformer
Nov 25, 2024 · In the world of electrical engineering, transformers, rectifiers, and inverters are fundamental components that enable the conversion and control

A high power factor rectifier associated with a ZCZVS PWM full
Jun 10, 2010 · This work presents the operation and design of a high power factor AC-DC-AC power supply rated at 2 kW operating at high switching frequency. Good power factor

Power Electronics
May 15, 2025 · Freewheeling Diode Three phase full converter is a fully controlled bridge controlled rectifier using six thyristors connected in the form of a full wave bridge configuration.

6 FAQs about [Full power rectifier inverter]
What is a rectifier & inverter?
Rectifier: Definition What is an Inverter? An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). While AC is the standard form of electricity used in most homes and industries, many power sources, such as solar panels and batteries, generate DC power.
What makes a good inverter & rectifier?
Load Consistency – Operating at full capacity improves efficiency, as both inverters and rectifiers perform best within specific load ranges. Component Quality – Higher-quality materials and more advanced circuitry yield better efficiency. Input Power Quality – Cleaner, stable power input improves performance and efficiency.
How does a rectifier convert AC to DC?
By converting AC from the main grid to DC, rectifiers provide the necessary power format for these devices. Rectifiers use components such as diodes, which allow current to flow in only one direction. When AC voltage is applied to a rectifier, the diodes restrict current flow to create a DC output. There are different types of rectifiers:
What are the different types of rectifiers?
Rectifiers come in two basic types: half-wave and full-wave. A half-wave rectifier allows electricity of only one polarity (positive or negative) to pass through, while a full-wave rectifier permits both. Electronic components called diodes form the heart of rectifier circuits, as they pass current in only one direction.
How does a full-wave rectifier work?
A full-wave rectifier uses two or four diodes (in a bridge configuration) to convert both halves of the AC waveform into positive DC. This results in a higher average output voltage and more efficient rectification than the half-wave method. The output is still a pulsating DC, but with less ripple.
What is a rectifier & how does it work?
A rectifier takes power from an AC source (like a home outlet) and converts it to DC, usually of a lower voltage. Radios, television receivers and power tools commonly contain rectifiers. Rectifiers come in two basic types: half-wave and full-wave.
Update Information
- Wholesale 1500 power inverter in Brunei
- What is the power of the inverter 390A
- Hanoi inverter energy storage power supply outdoor
- Inverter outputs negative power
- High voltage power inverter
- Inverter drags low power
- Approximate price of small power inverter
- DC plus inverter power
- 12v outdoor power supply with inverter
- West Africa Photovoltaic Power Generation Equipment Inverter
- Photovoltaic power generation system home inverter
- Outdoor portable power inverter
- Gel battery inverter power is low
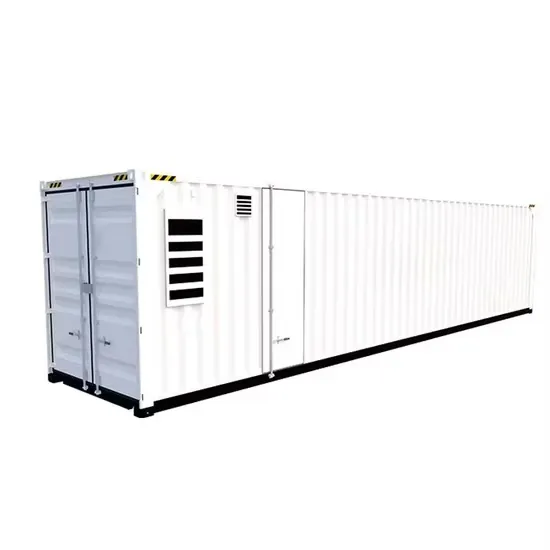
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
