
How to Optimize Your Inverter Settings for Solar
6 days ago · In the realm of solar energy, the inverter plays a pivotal role, transforming direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating

Differentiating between plant level and inverter level voltage control
Apr 1, 2022 · It can be seen that because of the nature of the network (i.e. long transmission lines), characteristics of the load, fast voltage control in the PV plant, and fast droop based
What is a Voltage Inverter? | Electrical Conversion – Sivo
Jan 9, 2025 · What is a Voltage Inverter? A voltage inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. The core function of a

Can You Stack Inverters to Change Battery Input Voltage?
Jul 30, 2025 · Here is the first question: I was at the trade show talking to a salesman about the Outback inverters and I mentioned I was planning to get an Outback 48 volt inverter.

Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
May 28, 2024 · How Do Inverters Work? Most modern inverters utilize some form of H-Bridge circuity to change the polarity of direct current. In most cases, the

DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design, Working &
Dec 26, 2024 · Inverters can maintain stable output voltage through internal control algorithms and power regulation mechanisms. Specifically: Constant

Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition,
Dec 16, 2024 · Inverter voltage is a voltage generated by the inverter after several electrons that converts a series of direct current (DC) into alternating current

Controlling input voltage to inverter
Jul 10, 2020 · We have an off-grid system with an older, "modified sine wave" inverter. When the charge controller goes into equalization mode, the voltage at the battery terminals exceeds the

How Do Inverters Convert DC Electricity To AC
May 5, 2023 · Inverters can also be used with transformers to change a specific DC input voltage into a completely different AC output voltage (either higher or

How may I change output Voltage of Phoenix Inverter
Apr 3, 2020 · In user manual is reported that Inverter Voltage is adjustable (210-245V). Because i have an automatic switch commutating inverter vs. grid, sometimes happen the main
6 FAQs about [Inverter can change voltage]
How do inverters convert DC voltage to AC voltage?
Most inverters rely on resistors, capacitors, transistors, and other circuit devices for converting DC Voltage to AC Voltage. In alternating current, the current changes direction and flows forward and backward. The current whose direction changes periodically is called an alternating current (AC). It has non-zero frequency.
What is the difference between an inverter and a converter?
An inverter is an electrical device, which converts DC power to AC power and either increases or decreases the voltage level accordingly. In comparison, a converter changes the voltage level but does not change its type. So in converters, an AC voltage would still be AC and a DC voltage would still be in DC.
How do Inverters change polarity?
Most modern inverters utilize some form of H-Bridge circuity to change the polarity of direct current. In most cases, the lower voltage DC current needs to be amplified to match the voltage of the AC it will be supplying.
Are inverters AC or DC?
So in converters, an AC voltage would still be AC and a DC voltage would still be in DC. Inverters are becoming more popular along with along with solar power systems where we get a low voltage DC supply to power ordinary appliances that either run on 110V or 220V AC. Inverters are used in a large number of electrical power applications.
What is a voltage inverter circuit?
The voltage inverter circuit is shown below, that uses a well known LM555IC timer chip. The schematic diagram divided into three parts, namely an oscillator, rectifier, and voltage regulator.An oscillator is used to convert DC into AC, a special type of rectifier is used to convert AC to DC and finally a voltage regulator.
How to control AC voltage in an inverter?
Basically, there are three techniques by which the voltage can be controlled in an inverter. They are, Internal control of Inverter. In this method of control, an ac voltage controller is connected at the output of the inverter to obtain the required (controlled) output ac voltage.
Update Information
- Can the inverter change to high voltage
- Inverter can change voltage
- Inverter outputs high current and high voltage
- What is the normal inverter voltage in Greece
- PV inverter power change
- Inverter for non-high voltage power users
- Inverter power AC voltage
- Rated voltage of the inverter
- Huawei inverter bipolar voltage to ground
- Inverter key point voltage
- High voltage inverter sm
- Inverter adjusts the front stage voltage
- Voltage generated by a 5 kW inverter
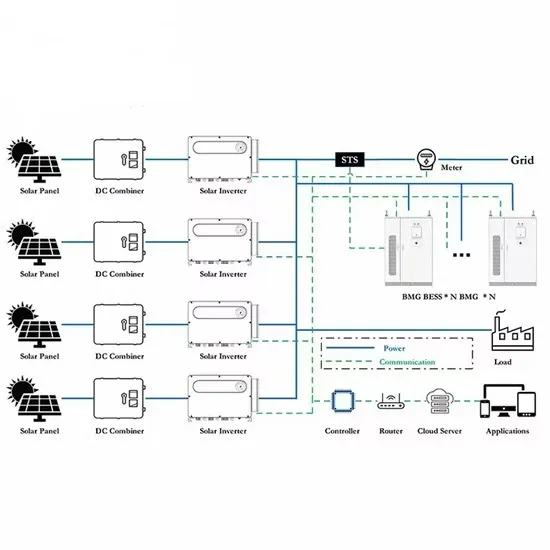
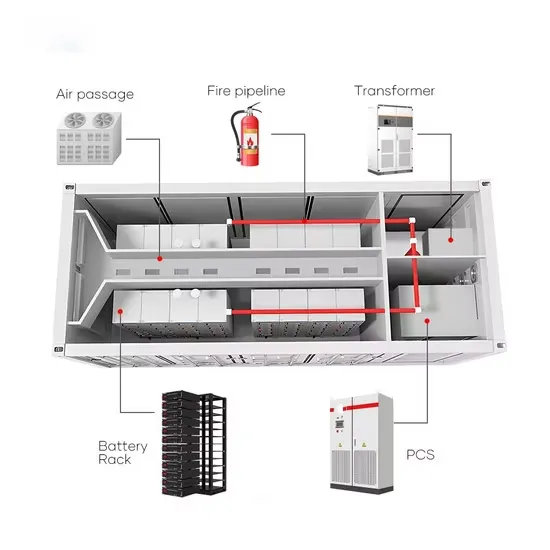
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
