
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply): What are they and why
A UPS is an electrical device that provides backup power via a battery to a load when regular utility power has been lost. Depending on the UPS, some can provide protection against

Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) – Definition, Block
Dec 16, 2022 · Learn about Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), its definition, block diagram, types, and various applications in this comprehensive guide.

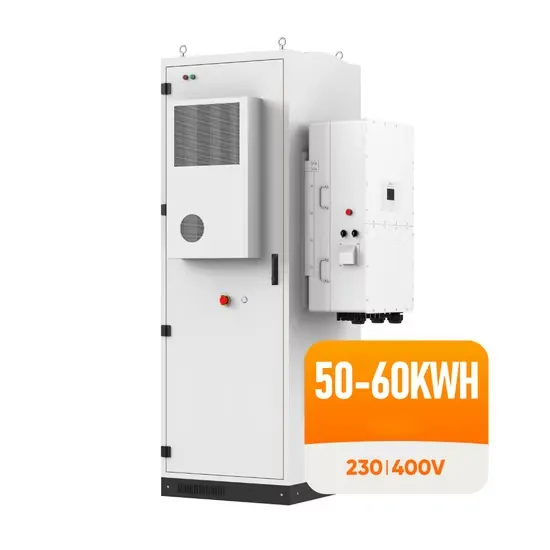
Dedicated Uninterruptible Power Supply for substations
UPS uninterruptible power supply is a third-generation power frequency pure online intelligent uninterruptible power supply (UPS) developed with new digital technology to meet the

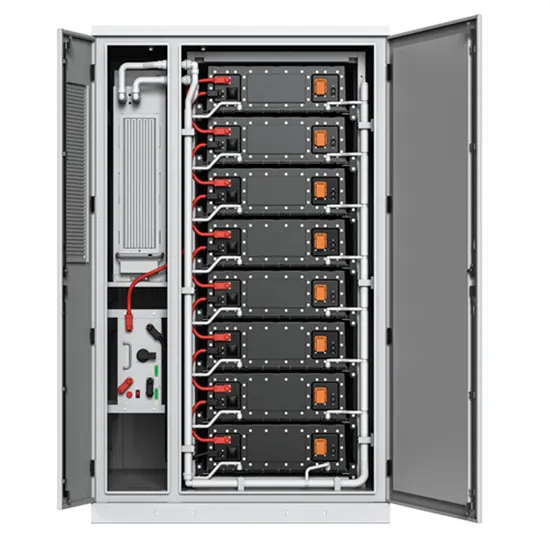
Mogadishu Uninterruptible Power Supply Plant Powering
May 12, 2025 · From voltage stabilization to renewable integration, the Mogadishu Uninterruptible Power Supply Plant represents more than backup power - it''s about enabling economic

Abdulaahi Mohamed
Electrical Engineer at mogadishu power supply · 工作经历: mogadishu power supply · 地点: 长沙 · 123 位领英好友。在领英 (一个拥有 10 亿会员的职业社区) 查看Abdulaahi Mohamed的职业档案。

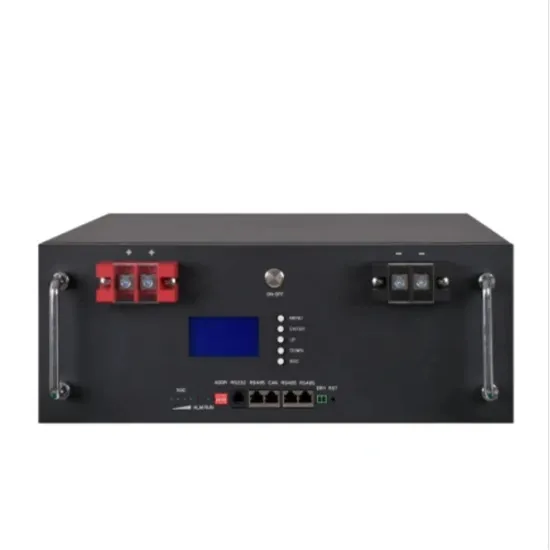
Overview of Uninterruptive Power Systems (UPS)
Dec 7, 2022 · Course Content An UPS system is an alternate or backup source of standby power with the electric utility company being the primary source. The UPS provides protection of load

Reliable UPS Solutions for Mogadishu Power Plants Ensuring
In regions like Mogadishu, where grid instability and extreme weather conditions threaten continuous power supply, industrial-grade uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems are

How does a UPS system work? | Schneider Electric Saudi Arabia
Battery Operation Mode is used when the utility/mains supply fails, the UPS transfers to battery operation with zero transferring time and supports the load with conditioned power from the

UPS selection, installation and maintenance
May 9, 2018 · Purpose of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) The purpose of this publication is to provide guidance for facilities engineers in selecting, installing,
6 FAQs about [Mogadishu substation UPS uninterruptible power supply]
Why should you install a UPS system in a substation?
With UPS installations in plants and substations, you can guard against downtime throughout your entire infrastructure. Avoid the irony of a power plant without power with uninterruptible power supplies to ensure the continuity of the utility’s supply and minimize disruptions.
What is an uninterruptible power system (UPS)?
An uninterruptible power system (UPS) is the central component of any well-designed power protection architecture. This white paper provides an introductory overview of what a UPS is and what kinds of UPS are available, as well as a comprehensive guide to selecting the right UPS and accessories for your needs. Topology 3
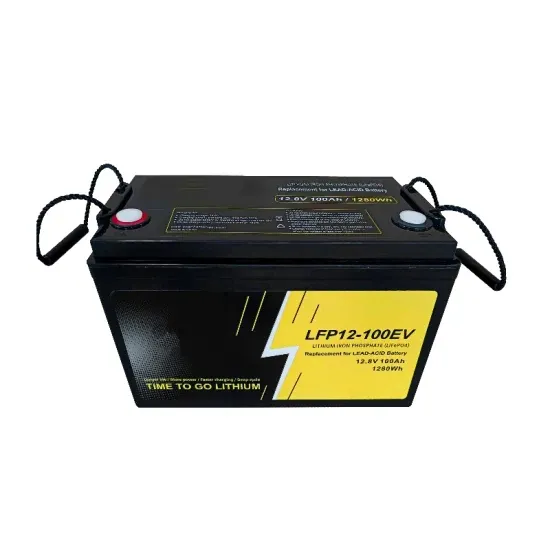
What is the difference between a UPS & energy storage?
UPS Definition: A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is defined as a device that provides immediate power during a main power failure. Energy Storage: UPS systems use batteries, flywheels, or supercapacitors to store energy for use during power interruptions.
What is a 3 phase UPS?
Three-phase power is generated and distributed to large commercial customers, with secondary customers, like homeowners, only receiving single phase power. A UPS’s power rating is the amount of load, in volt-amperes (VA), that it’s designed to support. UPSs are available with ratings as low as 300 VA and as high as 5,000,000 VA or more.
What is an ups & how does it work?
UPS can be used as a protective device for some hardware which can cause serious damage or loss with a sudden power disruption. Uninterruptible power source, Battery backup and Flywheel back up are the other names often used for UPS.
What are the different types of ups?
Two of the most popular single-conversion designs are standby and line-interactive. Standby UPSs allow IT equipment to run off utility power until the UPS detects a problem, at which point it switches to battery power. Some standby UPS designs incorporate transformers or other devices to provide limited power conditioning as well.
Update Information
- Estonia substation UPS uninterruptible power supply procurement
- Croatia substation ups uninterruptible power supply
- Sales of UPS uninterruptible power supply for substation in Alexandria Egypt
- Vienna UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply Agency Price
- Macedonia imported UPS uninterruptible power supply equipment
- Korea Busan Data Center UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply Company
- Vietnam Ho Chi Minh outdoor UPS uninterruptible power supply
- Ups uninterruptible power supply 6kw factory direct sales
- Huawei Ukraine Uninterruptible Power Supply UPS
- There is a three-phase UPS uninterruptible power supply
- Which UPS uninterruptible power supply is reliable in Dili
- Dare to UPS uninterruptible power supply 5kw
- Oslo UPS uninterruptible power supply recommendation
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
