
Terminal voltage analysis for the transformerless
Oct 23, 2019 · This study presents an analysis of the terminal voltage of the basic photovoltaic (PV) inverter topologies available in the literature. The presented

Terminal Voltage and Common Mode Voltage Analysis for Various PV
Nov 23, 2023 · Notably, as compared to normal PWM approaches, five-level common mode voltage source inverters (CMLIs) need less carrier waves. The study gives thorough insights

Experimental assessment of integral-type terminal sliding
Jun 1, 2024 · Abstract Due to the increasing global adoption of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems and their unpredictable power production behavior, as well as their interactions with

A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · In this review, the global status of the PV market, classification of the PV system, configurations of the grid-connected PV inverter, classification of various inverter types, and

The difference between PCS and energy storage
Nov 1, 2023 · The inverter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current. It is usually used in renewable energy power generation systems such

Photovoltaic inverter terminal symbols
Jul 20, 2021 · The inverter, in turn, is connected to the utility grid or electrical loads through another set of wires and cables. The solar panel and inverter connection diagram illustrates

An Introduction to Inverters for Photovoltaic (PV)
Jun 3, 2020 · Standalone inverters are for the applications where the PV plant is not connected to the main energy distribution network. The inverter is able to supply electrical energy to the

Photovoltaic inverter AC terminal
nections in a solar power system. It includes the solar panels, the DC di ng or disconnecting DC terminals. Maintenance and Repair: In a solar powe The active power control of photovoltaic

Article 690 SOLAR PHOTVOLATIC SYSTEM
A PV system that operates in parallel (interactive) with electrical utility power (or other power source, e.g., generator or wind system) through a utility-interactive inverter. Listed utility

Photovoltaic power station terminal inverter
Photovoltaic power station terminal inverter What is PV central inverter classification? PV central inverter classification For the usage of electric drives, first, in line-commutated inverters were

Solar Power Inverter Systems
Dec 7, 2022 · The specific components are included in a system are based on the type of photovoltaic system employed. Figure 1 shows a typical solar photovoltaic energy system.

PV Power Source Labeling in a SolarEdge system
Nov 30, 2022 · Introduction String design and installation is significantly different in a SolarEdge system when compared to a traditional string inverter. PV modules do not get connected in

What is a photovoltaic inverter?Selection, Principles & Future
Apr 28, 2025 · Definition of Photovoltaic Inverter. A photovoltaic inverter (PV Inverter), also known as a solar inverter, is a power electronic device. Its core function is to convert the direct current
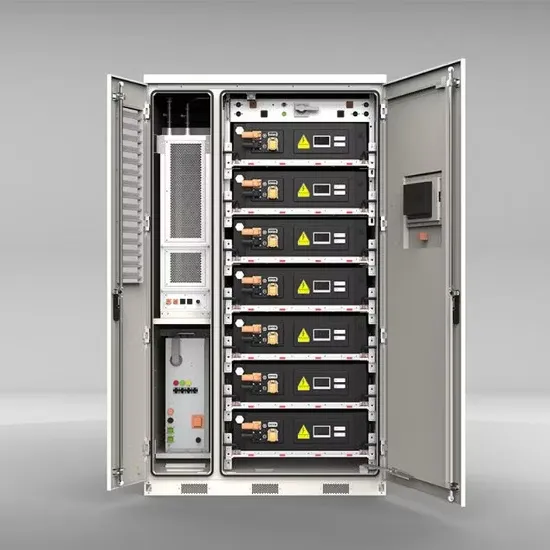

Photovoltaic power station terminal inverter
By using a reliable method, a cost-effective system has to be developed to integrate PV systems with the present power grid . Using next-generation semiconductor devices made of silicon
Terminal voltage analysis for the transformerless PV
Aug 7, 2024 · Abstract: This study presents an analysis of the terminal voltage of the basic photovoltaic (PV) inverter topologies available in the literature. The presented analysis utilises

The Complete Guide to Solar Inverters
Solar inverters are an essential component in every residential photovoltaic system. PV modules — like solar panels — produce direct current DC electricity using the photovoltaic effect.

6 FAQs about [Is the photovoltaic terminal system an inverter ]
What is a PV inverter?
On the other, it continually monitors the power grid and is responsible for the adherence to various safety criteria. A large number of PV inverters is available on the market – but the devices are classified on the basis of three important characteristics: power, DC-related design, and circuit topology.
What is a solar inverter?
Inverters - devices that convert DC power coming from the solar modules to AC power (necessary for grid) are critical components of any PV systems. Inverters convert DC power from the batteries or solar modules into 60 or 50 Hz AC power. As with all power system components, the use of inverters results in energy losses due to interferences.
Which type of Inverter should be used in a PV plant?
One-phase inverters are usually used in small plants, in large PV plants either a network consisting of several one-phase inverters or three-phase inverters have to be used on account of the unbalanced load of 4.6 kVA.
What is a power electronic based inverter?
In both standalone or grid-connected PV systems, power electronic based inverter is the main component that converts the DC power to AC power, delivering in this way the power to the AC loads or electrical grid.
How to pair a solar inverter with a PV plant?
In order to couple a solar inverter with a PV plant, it’s important to check that a few parameters match among them. Once the photovoltaic string is designed, it’s possible to calculate the maximum open-circuit voltage (Voc,MAX) on the DC side (according to the IEC standard).
What types of inverters are used in photovoltaic applications?
This article introduces the architecture and types of inverters used in photovoltaic applications. Inverters used in photovoltaic applications are historically divided into two main categories: Standalone inverters are for the applications where the PV plant is not connected to the main energy distribution network.
Update Information
- Photovoltaic intelligent power generation terminal inverter
- Belarusian micro photovoltaic inverter
- Tuvalu Photovoltaic Power Station Inverter
- Silicon Carbide Ultra-Thin Photovoltaic Inverter
- Does solar power require a photovoltaic inverter
- 1000 kW photovoltaic inverter
- Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter research and development
- 220 inverter can be connected to photovoltaic panels
- Kuala Lumpur Photovoltaic Water Pump Inverter Purchase
- Ireland three-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
- Photovoltaic inverter photovoltaic centralized procurement
- Valletta photovoltaic energy storage 10kw inverter price
- Micro photovoltaic inverter plug and play
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
