
Inverter Peak Power vs Rated Power: What it is
Apr 21, 2025 · The rated power is the power at which the inverter is stabilized over a long period, whereas the peak power is only used for short periods of

Common faults and solutions for inverters
May 23, 2025 · Common faults and treatment of inverters 1. Electrical quantity faults Electrical quantity faults are usually manifested as unstable output voltage, current or power of the

Common-Mode Voltage in Inverters: Effects and Reduction
Feb 25, 2022 · Key Takeaways The voltage difference between a power source and the neutral point of a load in inverters is called common-mode voltage. The effects of common-mode

Common Solar Power Inverter Problems and How to Balance
Aug 6, 2024 · Solar power has become a popular choice for many households and businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills. At the heart of most solar energy

What is the most common use of an inverter?
6 days ago · An inverter is one of the most essential components of modern power systems. Its primary function is to convert direct current (DC) electricity, which is commonly stored in

COMMON POWER OF PHOTOVOLTAIC INVERTER
ating heart in photovoltaic systems. String Inverter: Common and cost-effective; Suitable for systems without significant shading; it is crucial to consider not only the nominal power of the

COMMON POWER OF PHOTOVOLTAIC INVERTER
PV inverters convert DC to AC power using pulse width modulation technique. There are two main sources of high frequency noise generated by the inverters. strict regulation is imposed to

What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses,
Jan 25, 2025 · An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household

What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Jul 8, 2025 · Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and

How to Troubleshoot and Fix Common Inverter
6 days ago · Inverters are an essential part of many electrical systems, converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). When an inverter malfunctions,

Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They
Dec 17, 2019 · An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common

Find the Right Inverter Size: How Big An Inverter Do You need?
Dec 31, 2024 · When it comes to powering your devices through an inverter, one of the most critical aspects to consider is size—how big an inverter do you need? Whether you''re on an

Common Home Inverter Problems and How to Fix Them
Jan 21, 2025 · Learn about the most common home inverter problems and how to fix them. From battery issues to inverter malfunctioning, this guide provides easy solutions to keep your home

Analysis and Utilization of Common-Mode Voltage in Inverters for Power
Apr 17, 2023 · Common-mode voltage (CMV) exists at the terminal of motor windings when fed by voltage source inverters under pulsewidth modulation. For a long time, researchers devoted

Common Solar Inverter Failure Causes and Their
Jun 28, 2024 · Solar inverters play a crucial role in solar power systems to convert the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into Alternating Current

CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · What Is an Inverter? An inverter controls the frequency of power supplied to an AC motor to control the rotation speed of the motor. Without an inverter, the AC motor would

Common-Mode Voltage and Bearing Currents in PWM Inverters
May 30, 2014 · The aspects of common mode (CM) voltage and current in voltage source inverters and ac motors are illustrated in the chapter. The generation of CM voltages is a result
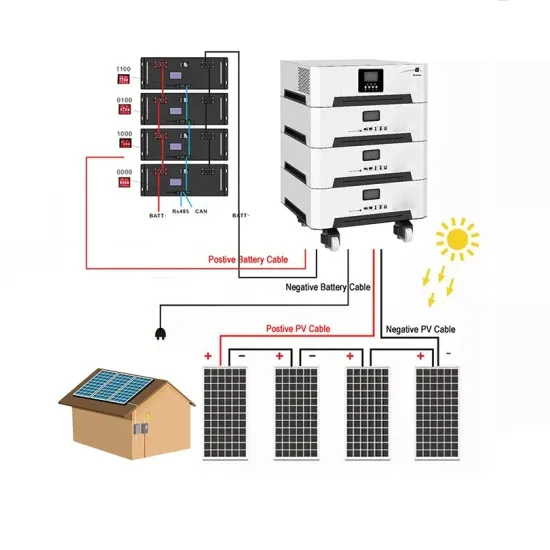
Power Inverter Troubleshooting – Common Problems and
Sep 24, 2024 · Power inverter troubleshooting can seem daunting, but by following the systematic approach outlined in this guide, you can diagnose and resolve most common problems.

Advanced power inverter topologies and modulation techniques for common
Apr 1, 2021 · PWM-controlled inverters produce substantial common-mode voltage (CMV). CMV causes motor/drive malfunctions and, eventually, system breakdowns. CMV can greatly be

Common Mode Power Control of Three-Phase Inverter for
Jul 26, 2021 · The purpose of this article is to investigate the potential of obtaining an auxiliary dc output from the common-mode switching harmonics of a three-phase inverter without access
6 FAQs about [Common power of inverter]
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
What are inverters used for?
Inverters are essential components in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and whole-house backup systems. They provide seamless power during outages by converting stored battery power to AC electricity. Critical applications include:
How does an inverter work?
The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power and again creates AC power from the converted DC power using PWM control. The inverter outputs a pulsed voltage, and the pulses are smoothed by the motor coil so that a sine wave current flows to the motor to control the speed and torque of the motor.
What does a solar inverter do?
Inverters are essential components in solar energy systems, converting direct current (DC) from solar panels or batteries into alternating current (AC) compatible with household appliances and the electrical grid. This conversion is vital since most household devices and grids operate on AC power.
What are the different types of AC inverters?
The three most common types of inverters made for powering AC loads include: (1) pure sine wave inverter (for general applications), (2) modified square wave inverter (for resistive, capacitive, and inductive loads), and (3) square wave inverter (for some resistive loads) (MPP Solar, 2015).
What are inverter specifications?
Specifications provide the values of operating parameters for a given inverter. Common specifications are discussed below. Some or all of the specifications usually appear on the inverter data sheet. Maximum AC output power This is the maximum power the inverter can supply to a load on a steady basis at a specified output voltage.
Update Information
- Power plant protection screen battery inverter
- Danish photovoltaic power station inverter
- Guatemala City power frequency inverter custom manufacturer
- Inverter power is greater than battery power
- How much power inverter can be made with 50va
- Inverter general power
- Inverter that can increase motor power
- Ups inverter power components
- Household photovoltaic panel inverter high power
- Rwanda Photovoltaic Power Generation Equipment Inverter
- Inverter exceeds power
- How much power can the inverter use
- Wholesale 200w power inverter in Chad
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
