
What is the Difference Between UPS and Inverter?
Aug 16, 2025 · UPS (Uninterruptible power supply) is a system which uses a battery and an inverter to provide continuous power supply. When is no power, the battery (with the help of
How to Convert a UPS Into an Inverter | Step-by-Step Guide
Dec 21, 2023 · An inexpensive and sustainable alternative power source can be made by transforming a UPS into an inverter. This practical method comes in particularly handy for
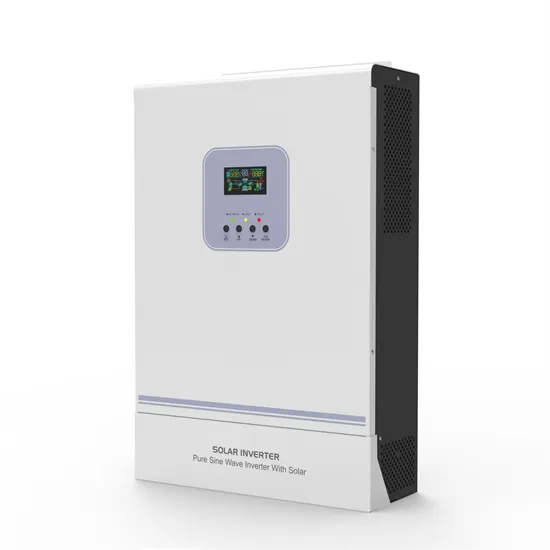

Difference between Inverter and UPS
Jun 29, 2022 · The most significant difference between a UPS and an inverter is that a UPS is a more expensive device used for supplying backup power to the sensitive electrical and

Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What
3 days ago · The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current

Difference between UPS and Inverter – Which is better?
Jan 10, 2025 · Response Time: One of the most significant advantages of a UPS is its instantaneous response to a power outage. Typically, a UPS will switch to battery power within

Difference between UPS and Inverter – Which is better?
Jan 10, 2025 · Understanding UPS and Inverters What is an Inverter? An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It allows power to be

6 FAQs about [UPS power and inverter output power]
What is a ups inverter & how does it work?
The UPS is an electrical device that provides power to the load when the main power fails. The inverter converts the unidirectional current into bidirectional. Main function is to convert AC power to DC power. Offline, Online, Line interruptive or Standby UPS. Stand Alone and Grid Tie Inverter. Directly connected to the appliances.
Can a ups be an inverter?
Good to know: A UPS can be an inverter but an inverter can’t be a UPS as Inverter is the part of UPS (uninterruptible power supply). Related Posts: What is UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)?
What are the advantages of a ups vs an inverter?
Response Time: One of the most significant advantages of a UPS is its instantaneous response to a power outage. Typically, a UPS will switch to battery power within milliseconds. 1. Functionality The primary function of both a UPS and an inverter is to provide backup power during an outage.
What is ups mode in an inverter?
This ensures uninterrupted power supply to connected devices, protecting them from data loss, equipment damage, and disruption. The UPS mode in an inverter provides similar functionality to a dedicated UPS, combining the power conversion capability of the inverter with the automatic switchover feature of a UPS.
What is ups (uninterruptable power supply)?
UPS (Uninterruptible power supply) is a system which uses a battery and an inverter to provide continuous power supply. When is no power, the battery (with the help of inverter)will help to power up all the connected AC devices and run with UPS.
What is the difference between online UPS and inverter?
Functionality: The difference is that most Online UPS have an inverter section and rectifier designed to provide instant quality backup power during outages. Most of them have an in-built battery which is suitable to power loads for lesser durations as a standalone device. However, when the load requirement is higher, a UPS relies on batteries.
Update Information
- How much AC power does the inverter output
- Inverter rated AC output power
- Increase the output power of household inverter
- UPS inverter charging power
- Wind power inverter output voltage
- Is the three-phase output of the inverter safe
- High voltage power supply full bridge inverter price
- Beiya Power Inverter Price
- Does the inverter output a sine wave
- Inverter rear bridge output voltage is too low
- How much does a high power inverter cost
- 12v outdoor power supply with inverter
- Huawei inverter 5000 watt high power
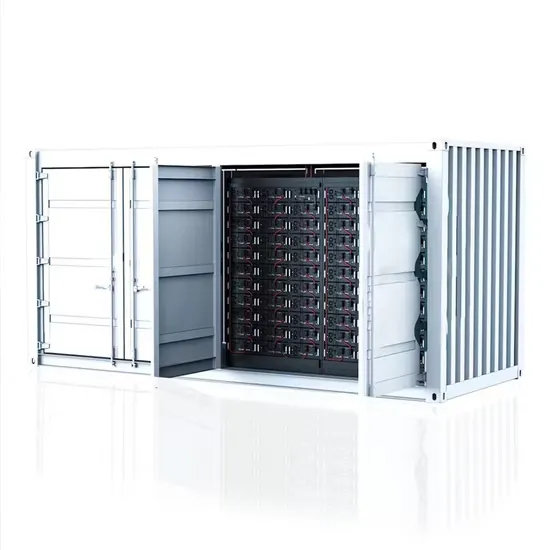
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
