
Difference Between UPS and Inverter – Which is
Oct 12, 2023 · Basic difference between UPS & Inverter discussed. Factors you need to consider when buying them - It depends on the number of devices &
What Is the Difference Between a UPS and an Inverter?
Inverters are better suited for providing extended backup power, switching from on-grid to battery electricity a little slower than a UPS. For a versatile and eco-friendly alternative, consider

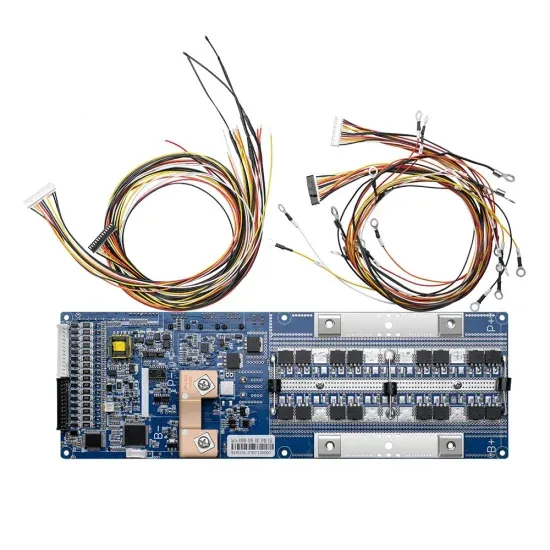
UPS Charging Power Supply Explained: How Leyu Ensures
Normal Mode: When mains power is stable, the UPS acts as a voltage stabilizer, filtering fluctuations and charging its internal battery. Backup Mode: During outages, the UPS

How To Charge Inverter Battery | Tips & Charging Time
Oct 23, 2024 · Charging a UPS is slightly different from charging an inverter due to the differences in their operational design. While both are backup solutions, UPS systems typically provide

power consumption of UPS with respect to battery charging
Typically speaking no electric device can take more than 80% of its input breaker size. In your case APC calls for a 40 amp input breaker and a 32 amp bypass breaker. So you would take

ECO-WORTHY 600W Pure Sine Wave Inverter Charger,
Aug 26, 2024 · 600W Inverter & 25A Charger 2-in-1: ECO-WORTHY inverter charger combines both an inverter and battery charger in one unit, delivering a powerful 25A charging capability

Buy Super Power Digital Inverter/Home UPS 900 | Microtek
Super Power Digital UPS Model is a Micro Controller design based, LARGEST SELLING SERIES of Extended Backup External Battery UPS Systems. It comes with many user friendly features.

UPS Battery System vs Inverter, Comprehensive Guide
Nov 22, 2023 · Understanding UPS Battery Systems Redway starts by unraveling the intricacies of UPS battery systems, delineating them as uninterruptible power supplies. Comprising

6 FAQs about [UPS inverter charging power]
What is the difference between charging a ups and charging an inverter?
Charging a UPS is slightly different from charging an inverter due to the differences in their operational design. While both are backup solutions, UPS systems typically provide immediate power transition, which can affect how they charge. To charge a UPS, simply connect it to a reliable power outlet.
How long does it take to charge a ups & inverter?
The UPS and inverter charging time varies based on several factors, including battery capacity and charger efficiency. Typically, an inverter may take anywhere from 6 to 12 hours to full charge a standard tubular battery. The key influencer here is the charger’s output capacity—higher capacities result in faster charging times.
What is fast charging in inverter/ups?
Fast Charging in Inverter/UPS: A Game-Changer for Power Cuts where the electricity availability is deficient. There are areas in the world like Nigeria, Yemen, Afghanistan, Syria, etc., where the power coming from the grid is unstable, and the timing for grid power availability is minimal.
Can a ups inverter be connected to a battery?
Yes. While it is recommended that you keep the inverter as close to the batteries as possible, the load can be connected with an extension cord and located up to 200 feet away without signal loss. How is an inverter different than a UPS? A UPS typically includes the battery and battery charger in one standalone unit.
How do ups charge?
While both are backup solutions, UPS systems typically provide immediate power transition, which can affect how they charge. To charge a UPS, simply connect it to a reliable power outlet. Most modern UPS systems are designed to charge automatically once connected.
How do I avoid overcharging my inverter/UPS battery?
Overdischarging and overcharging can substantially shorten the life and efficiency of your battery. Turning off redundant devices during power outages might help prevent excessive battery depletion. Similarly, to avoid overcharging, ensure that your inverter/UPS charging process is appropriately regulated and monitored.
Update Information
- UPS power and inverter output power
- Charging pile inverter power
- Ups inverter power components
- Charging inverter sine wave power frequency inverter
- Inverter high power rear stage
- Will the inverter affect photovoltaic power generation
- High quality wholesale 1500 power inverter supplier
- Swedish photovoltaic power station inverter manufacturer
- Vanuatu Inverter Intelligent Energy Storage Power Supply
- Wellington power frequency inverter price
- Democratic Republic of Congo off-grid power frequency 15kw inverter
- Charging pile inverter supplier
- Tuvalu Photovoltaic Power Station Inverter
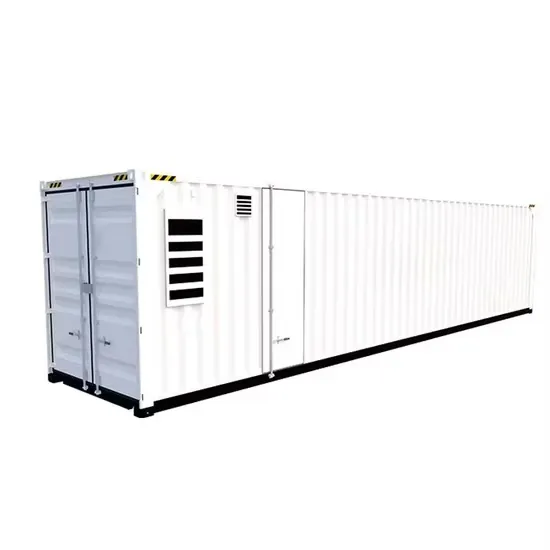
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
