
Fundamental‐Frequency Bus‐Impedance Analysis of Power
Jun 16, 2025 · This article investigates how the placement of grid-forming (GFM) and grid-following (GFL) inverters influences the equivalent fundamental-frequency impedance at

Power system reduction techniques for planning and
Feb 1, 2024 · The main contribution of this paper, in addition to a thorough review of power system reduction techniques, is the inclusion of new emerging components in modern power

Optimizing power quality in interconnected renewable
May 25, 2024 · The optimization of power quality (PQ) in interconnected renewable energy systems (RES) is examined in this paper, with a special focus on photovoltaic (PV) and wind

Review of Methods for Reducing Circulating Currents in
Jan 20, 2023 · This study aims to investigate the circulating current in the parallel three-level inverters and compare the performance of the reduction methods in terms of effectiveness,

Grid-connected renewable energy sources: Review of the
Apr 20, 2020 · The review is conducted by a comparing of the key requirements related to voltage stability, frequency stability, voltage ride-through (VRT), power quality, active and reactive

Model Reduction and Dynamic Aggregation of Grid-Forming Inverter
Dec 16, 2022 · This paper presents a model-order reduction and dynamic aggregation strategy for grid-forming inverter-based power networks. The reduced-order models preserve the network

Inertia and the Power Grid: A Guide Without the Spin
Jun 16, 2020 · Grid frequency, which is a measure of the balance of supply of electricity and demand, can drop if a large power plant or transmission fails. Inertia resists this drop in

(PDF) Model Predictive Control of Grid-Connected Inverters
Sep 1, 2013 · This paper presents a model-predictive direct power control (MPDPC) strategy for a grid-connected inverter used in a PV system. Thus is aimed at use in distributed generation.
A review on single-phase boost inverter technology for low power grid
Feb 1, 2024 · In this section, we present an analysis and discussion of different transformerless single-stage boost inverters with respect to power decoupling, power losses, size, cost, and

Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes,
Jan 1, 2024 · Grid-connected PV inverters have traditionally been thought as active power sources with an emphasis on maximizing power extraction from the PV modules. While

Single phase grid-connected inverter: advanced control
Jul 28, 2025 · Advanced control techniques such as proportional-resonant control, deadbeat control, and model predictive control are analyzed for their effectiveness in achieving high
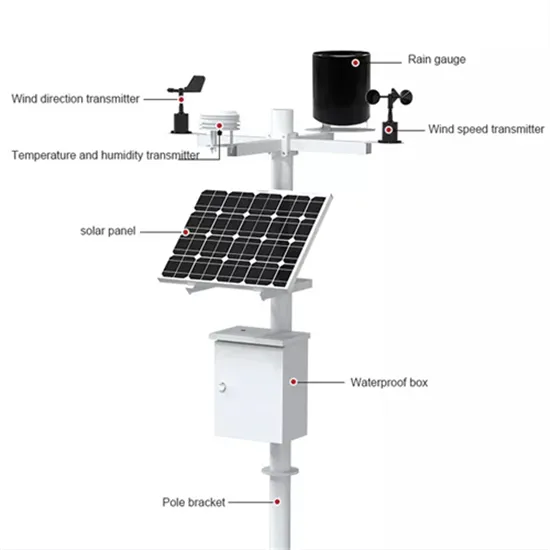

A Comprehensive Review of Inverter Standards and
Jan 22, 2025 · An inverter is a crucial component in grid-connected PV systems. This study focuses on inverter standards for grid-connected PV systems, as well as various inverter
A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · The requirements for the grid-connected inverter include; low total harmonic distortion of the currents injected into the grid, maximum power point tracking, high efficiency,

Model Predictive Control of Grid-Connected Inverters for
Dec 4, 2018 · Using this method, a grid-connected inverter system can achieve flexible power regulation and switching frequency reduction. The controller is simple and effective.

(PDF) Model Predictive Control of Grid-Connected Inverters
Sep 1, 2013 · Model Predictive Control of Grid-Connected Inverters for PV Systems With Flexible Power Regulation and Switching Frequency Reduction September 2013

Penetration and control of grid-forming (GFM) inverter in
Dec 1, 2024 · Grid-forming (GFM) inverter development and applications are gaining significant attraction because of their ability to maintain quality power-grid operations. GFM inverter,

Model Reduction and Dynamic Aggregation of Grid
Dec 2, 2022 · First, Kron reduction is used to reduce the dimensions of the electrical network model. Next, dynamic aggregate models are developed for parallel-connected inverters.

Leakage Current Reduction in Single-Phase Grid
The power that is injected into the grid varies in time to twice the frequency of the grid; however, the energy extracted from the PV must be constant to maximize energy extraction [45],

Analytical distributed PV inverter reactive power support
Aug 30, 2024 · This paper deals with the reduction of power losses and voltage deviation in radial electrical power grids. To address these challenges, an innovative approach is proposed for

Critical review on various inverter topologies for
Feb 22, 2021 · Different control strategies for balanced and unbalanced grid integration such as,,, fault ride through, and unified power flow control are

A review on modulation techniques of Quasi-Z-source inverter for grid
Dec 1, 2024 · The 3L-NPC inverter has been widely adopted in medium and high-power applications, improving power quality and efficiency. Authors in [33], confirmed that the

Coordination of smart inverter-enabled distributed energy
Dec 1, 2024 · Smart inverters offer dynamic reactive power control, which can be harnessed to aid voltage regulation efforts. Volt-VAr control allows smart inverters to adjust reactive power

6 FAQs about [Inverter power reduction and frequency reduction for grid connection]
Can grid-connected PV inverters improve utility grid stability?
Grid-connected PV inverters have traditionally been thought as active power sources with an emphasis on maximizing power extraction from the PV modules. While maximizing power transfer remains a top priority, utility grid stability is now widely acknowledged to benefit from several auxiliary services that grid-connected PV inverters may offer.
What is a grid-connected inverter?
In the grid-connected inverter, the associated well-known variations can be classified in the unknown changing loads, distribution network uncertainties, and variations on the demanded reactive and active powers of the connected grid.
What is a model-order reduction and dynamic aggregation strategy for grid-forming inverter-based power networks?
This paper presents a model-order reduction and dynamic aggregation strategy for grid-forming inverter-based power networks. The reduced-order models preserve the network current dynamics as well as the action of the inverter current-reference limiter.
What is a pic-based frequency response strategy for grid forming inverter?
A PIC-based frequency response strategy for grid forming inverter is proposed. PIC strategy can enhance the frequency stability of IMGs under large disturbances. PIC strategy can be implemented in IMGs and complex multi-machine systems.
Do reduced-order models preserve grid-forming inverter-based power networks?
Abstract—This paper presents reduced-order models for grid-forming inverter-based power networks that preserve the network current dynamics as well as the action of the inverter current-reference limiter.
Should auxiliary functions be included in grid-connected PV inverters?
Auxiliary functions should be included in Grid-connected PV inverters to help maintain balance if there is a mismatch between power generation and load demand.
Update Information
- Power frequency inverter self-grid connection
- High frequency inverter power supply
- San Marino communication base station inverter grid connection maintenance
- Inverter grid connection address of Argentina mobile energy storage site
- Mauritania communication base station inverter grid connection planning
- Slovenia communication base station inverter grid connection approval
- Palestine 48v power frequency inverter
- Bandar Seri Begawan 5G communication base station inverter grid connection construction project
- El Salvador 5G communication base station inverter grid connection bidding
- Off grid solar power inverter in Israel
- Castrie power frequency off-grid inverter price
- USA communication base station inverter grid connection address
- Manama communication base station inverter grid connection
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
