
What is 5g base station architecture
Aug 21, 2024 · A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN). It facilitates wireless communication between user

Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base Station
Jan 17, 2025 · 5G networks use a broader range of spectrum resources, particularly the millimeter-wave bands (24 GHz and above). Base station chips must be capable of efficiently

Location of 5G base station antenna in substation taking into
Oct 16, 2024 · Abstract Aiming at the engineering problem that 5G base station antenna is difficult to locate efficiently in complex electromagnetic environment, a two-stage positioning method of

5GNR Base Station Measurements in the Field
Apr 4, 2024 · Network operators who have historically built previous generation cellular networks, including GSM, 3G (WCDMA), and LTE have years of experience in testing new base station

11410-02891A_5GNR_Base_Station_AN-v3 dd
Nov 15, 2022 · Network operators who have historically built previous generation cellular networks, including GSM, 3G (WCDMA), and LTE have years of experience in testing new

Adaptive beamforming scheme for coexistence of 5G base station
Apr 1, 2025 · The Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics published a report evaluating the impact of 5G communications interference on low-range radar altimeter operations in the U.S.
What Is 5G Base Station?
Apr 8, 2025 · Base stations, also called public mobile communication base stations, are interface devices for mobile devices to access the Internet. They are also a form of radio stations, which

Understanding Base Transceiver Stations: The Backbone of
Jan 1, 2025 · Simply put, a base transceiver station (BTS) is a vital component of mobile networks, serving as the communication hub that connects your mobile phone to the wider

Which RF Technologies Are Shaping 5G Base Stations?
Apr 24, 2025 · 5G base stations are the backbone of the 5G network, transmitting and receiving radio signals across various frequency bands to provide connectivity to mobile devices.

Learn What a 5G Base Station Is and Why It''s Important
A 5G base station is the heart of the fifth-generation mobile network, enabling far higher speeds and lower latency, as well as new levels of connectivity. Referred to as gNodeB, 5G base

6 FAQs about [Is the 5G signal base station a radio ]
What are the different types of 5G NR base stations?
This article describes the different classes or types of 5G NR Base Stations (BS), including BS Type 1-C, BS Type 1-H, BS Type 1-O, and BS Type 2-O. 5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB.
What is a 5G base station?
As the world continues its transition into the era of 5G, the demand for faster and more reliable wireless communication is skyrocketing. Central to this transformation are 5G base stations, the backbone of the next-generation network. These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises.
What is 5G NR BS?
5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB. These 5G NR BS operate in two frequency ranges: FR1 and FR2. (../../assets/5G-NR-BS-Channel-Bandwidths.jpg). Table 1: Frequency Ranges
What are the components of a 5G core network?
The key components of a 5G core network are seen here: User Equipment (UE): 5G cellular devices, such as smartphones, connect via the 5G New Radio Access Network to the 5G core and then to the internet. Radio Access Network (RAN): Coordinate network resources across wireless devices.
What are base stations in 4G LTE networks called?
The base stations in 4G LTE networks are called either evolved Node B or eNodeB. You’ll find that eNodeB is usually reviated as eNB in 5G network architecture diagrams, and gNodeB as gNB. It helps to keep mind that a base station called eNB is for 4G, and gNB is for 5G.
What is 5G network architecture?
The increased data bandwidth is enabled by these two new radio frequency ranges: Range 1: 450 MHz – 6000 MHz – overlaps with 4G LTE frequencies and termed as sub-6 GHz. 5G network architecture is based on entirely new standards introduced by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
Update Information
- Chisinau Communication 5g signal tower base station construction
- Huawei 5g radio base station access
- Communication 5g base station equipment update
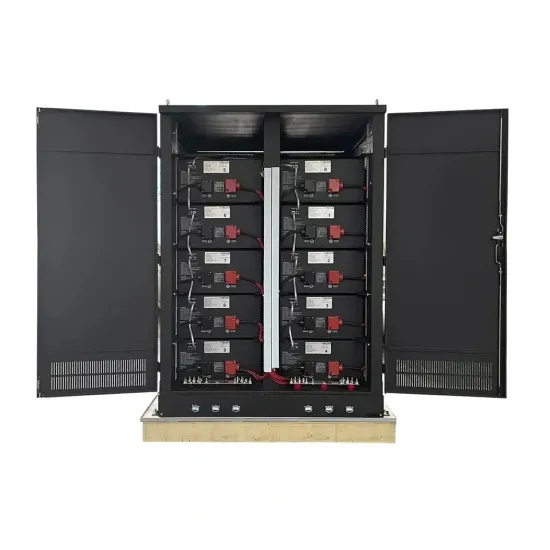
- China Communications 5G Base Station Related Battery Situation
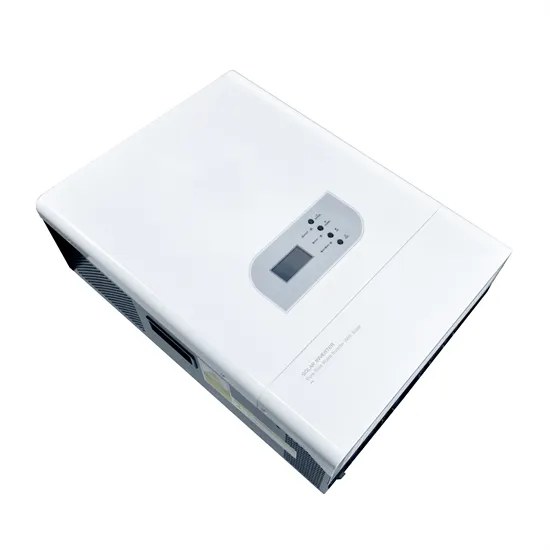
- 5g base station power optimization concept
- Tehran 5g base station electricity consumption
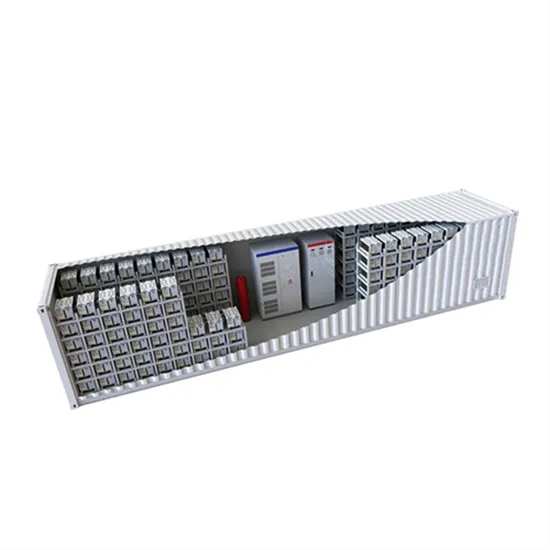
- Burundi 5g base station outdoor photovoltaic integrated system cabinet
- Oslo 5g base station communication project
- Beirut 5g communication base station 125kWh
- 5g base station battery ranking
- How many 5G base station photovoltaic power generation system points are there in Vaduz
- State Grid enters 5g base station
- 5g communication base station inverter grid-connected construction facilities
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
