Base Transceiver Station: Core Functionality Explained
Apr 5, 2025 · Discover what a Base Transceiver Station is and how it''s pivotal in mobile communication networks. Unlock the essentials of BTS functionality here.

Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of
May 16, 2024 · Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless

What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base
Aug 16, 2022 · A base station is referred to a stationary trans-receiver used in telecommunications that serves as the primary hub for connectivity of wireless
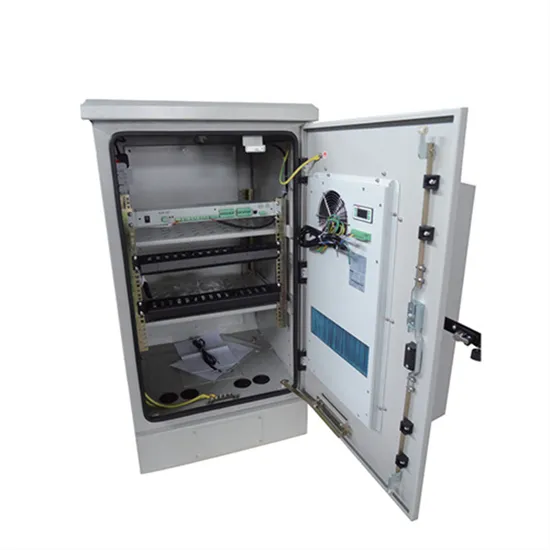

Understanding Base Transceiver Stations: The Backbone of
Jan 1, 2025 · What is Base Transceiver Station? A Base Transceiver Station (BTS) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between a mobile device and a network.

The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The Key to
Aug 7, 2024 · Base station, also known as BTS (Base Transceiver Station), is a key device in wireless communication systems such as GSM. Equipped with an electromagnetic wave
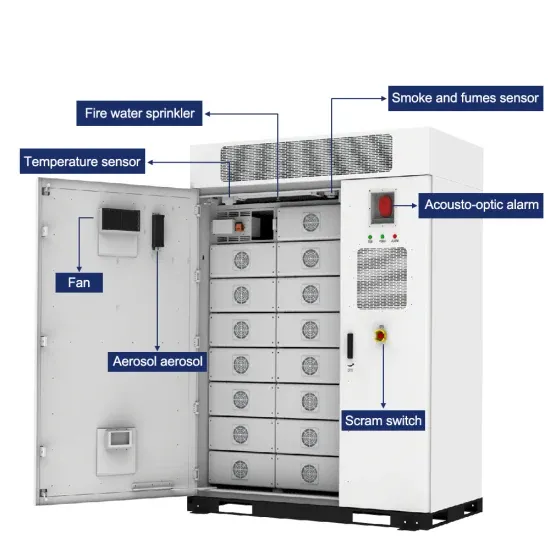

What is Telecommunication Base Station | China Hop
Generally speaking, a base station consists of three antennas, each transmitting signals in a 120 degree direction towards the surrounding area, which together provide seamless coverage of

6 FAQs about [What is a telecommunications company s base station ]
What is a base station in telecommunications?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices. A base station serves as a central connection point for a wireless device to communicate.
What is a base station in a wireless network?
At the heart of wireless communication networks are base stations, which act as the gateway between wireless devices and the network infrastructure. Base stations are responsible for transmitting and receiving data to and from wireless devices, as well as managing network resources and ensuring reliable and efficient communication.
What does a base station do?
Base stations are responsible for transmitting and receiving data to and from wireless devices, as well as managing network resources and ensuring reliable and efficient communication. The basic function of a base station is to convert wireless signals into digital signals that can be transmitted over a wired network infrastructure.
Why are base stations important for modern telecommunications?
In summary, base stations are critical for modern telecommunications as they serve as the link between mobile devices and the extensive network infrastructure that spans the globe. The strategic deployment and ongoing improvement of these stations are essential for maintaining global connectivity.
How does a wireless device communicate with a base station?
When a wireless device, such as a mobile phone, communicates with a base station, the device sends a signal to the base station, which converts the signal into digital form and sends it to the network. Similarly, when the network sends data to the device, the base station converts the digital data into a wireless signal that the device can receive.
Is a base station a transmitter or broadcast point?
Base stations are generally a transceiver, capable of sending and receiving wireless signals; otherwise, if they only transmitted signals out, they would be considered a transmitter or broadcast point. A base station will have one or more radio frequency (RF) antennas to transmit and receive RF signals to other devices.
Update Information
- What power supply does the telecommunications base station use
- Malaysia National Telecommunications Base Station Wind Power
- What does it mean to tune the supercapacitor of a communication base station
- What is the use of base station power module
- Huawei Communication Base Station Inverter Grid-connected Equipment Company
- What is the resistance of the communication base station
- What communication base station inverters are connected to the grid in the Democratic Republic of Congo
- What communication base station inverters are connected to the grid in Belgium
- What is the reason for the hybrid energy of Kyiv communication base station
- What is a 5G communication base station like
- What is the electromagnetic battery of a communication base station
- What is the power of the solar energy storage ESS of the communication base station
- What to do if the 5G base station speed is slow
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
