
What Is the Photovoltaic Effect?
The science behind the photovoltaic effect intertwines with some of the core principles of modern physics. At the heart of this phenomenon is the photoelectric effect, a process discovered in
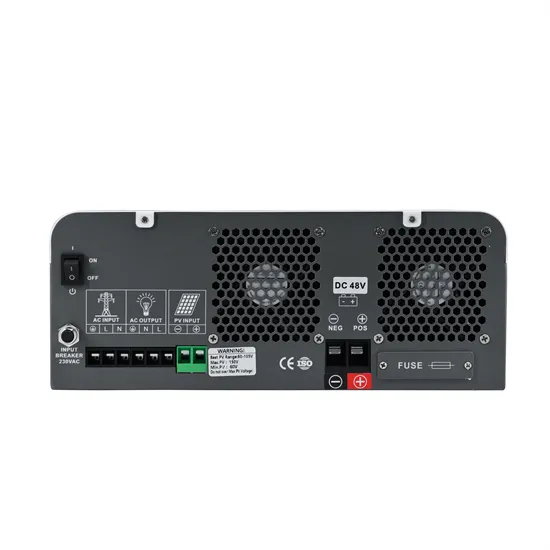

The Effect Of Numbers Of Inverters In Photovoltaic Grid
Oct 24, 2015 · Abstract: The DC/AC inverters are used in grid-connected PV energy production systems as the power processing interface between the PV energy source and the electric

what is PID and how to prevent and repair PID phenomenon
Jun 11, 2022 · Option 3: Use the forward bias voltage scheme to fix the PID effect This solution is suitable for distributed photovoltaic power stations composed of single or multiple string

What is the prd effect of photovoltaic inverter
In the future, with demand for renewable energy grows, grid-connected PV inverters will become increasingly high voltage and high power. High voltage and high power applications will

The effect of rain on photovoltaic systems
Dec 1, 2021 · In other research fields, several works can be found about the effect of rainwater drops on leaves [16, 17] or on other surfaces in presence of incident solar radiation [18], but
Fuzzy quasi‐PRD control for the photovoltaic
Jan 15, 2019 · When the photovoltaic inverter is connected to a weaker power grid, the bandwidth of the control system of the inverter will be reduced. Using

Fuzzy quasi-PRD control for the photovoltaic inverter with
With the development of photovoltaic power generation technology, a large number of micro-power grid with distributed generation system have appeared in remote areas. It has the

Adaptive quasi-PRD control method of grid-connected PV inverter
Jun 5, 2015 · The high grid impedance in weak grid will lead to small bandwidth of control system and poor control performance of PV inverter. To solve this problem, this pap

Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes,
Jan 1, 2024 · The proliferation of solar power plants has begun to have an impact on utility grid operation, stability, and security. As a result, several governments have developed additional

Fuzzy quasi-PRD control for the photovoltaic inverter
Sep 12, 2024 · This is called the weak grid [2]. Research shows that the impedance characteristics of weak power grid is not only safe and stable operation of photovoltaic grid

Fuzzy quasiâ PRD control for the photovoltaic inverter
Jan 15, 2021 · This is called the weak grid [2]. Research shows that the impedance characteristics of weak power grid is not only safe and stable operation of photovoltaic grid inverter [3, 4], and
Power Factor and Grid-Connected Photovoltaics
Nov 23, 2020 · Power Factor and Grid Connected PV Systems Most grid connected PV inverters are only set up to inject power at unity power factor, meaning they only produce active power.

Fuzzy quasi-PRD control for the photovoltaic inverter with
Oct 24, 2018 · When the photovoltaic inverter is connected to a weaker power grid, the bandwidth of the control system of the inverter will be reduced. Using the traditional PR control to solve

Harmonic characteristics and control strategies of grid
Nov 1, 2022 · To investigate the harmonic characteristics of a photovoltaic (PV) system connected to the weak grid, a passive impedance network is constructed using the impedance model of a

Effect of PV-inverter''s Reactive Power Injection and Location
Mar 11, 2022 · This paper presents the effects of PV grid-connected inverter installation in low-voltage distribution power systems; its reactive power and locations were cons

Effect of Reactive Power on Photovoltaic Inverter
Sep 4, 2019 · Abstract — This paper performs research on predicting Photovoltaic (PV) inverters reliability and lifetime based on thermal cycling. Thermal cycling is considered the most

Fuzzy quasiâ PRD control for the photovoltaic inverter
Jan 15, 2021 · To solve this problem, this paper puts forward the fuzzy quasi-PRD control method of the single-phase photovoltaic grid inverter in the weak. It not only realises the zero steady

What does the prd effect of photovoltaic inverter mean
In case you are dealing with unexpected and unreasonable power loss in your photovoltaic plant,you may be experiencing the PID effect in the PV modules. Potential induced

4 FAQs about [What is the prd effect of photovoltaic inverter]
Do grid connected PV inverters reduce reactive power?
There is therefore an incentive for these customers to improve the power factor of their loads and reduce the amount of reactive power they draw from the grid. Most grid connected PV inverters are only set up to inject power at unity power factor, meaning they only produce active power.
How does a grid connected PV inverter affect the power factor?
Most grid connected PV inverters are only set up to inject power at unity power factor, meaning they only produce active power. In efect this reduces the power factor, as the grid is then supplying less active power, but the same amount of reactive power. Consider the situation in Figure 5.
How much power does a PV system produce?
Figure 7 (following page) shows the factory with the inverter set to a power factor of 0.95 - leading. The PV system is now producing 57kW of active power and 18.7kVAr of reactive power, reducing the amount of both active and reactive power from the grid.
How important is power factor correction in grid-connected PV?
As the level of Grid-Connected PV penetration continues to rise, the importance of power factor and power factor correction is going to become increasingly relevant both from the perspective of the grid and the customer.
Update Information
- What is the lifespan of a photovoltaic inverter
- What is the impedance of the photovoltaic inverter
- What is the lifespan of a 20kw photovoltaic inverter
- What is the capacity of the photovoltaic inverter
- Photovoltaic inverter 14kw
- Photovoltaic power station inverter recommendation
- How much photovoltaic can an 80kw inverter drive
- Small photovoltaic portable inverter
- Photovoltaic energy storage inverter in Mombasa Kenya
- Photovoltaic inverter heating
- Photovoltaic off-grid inverter merchants
- Household photovoltaic inverter 5000w price
- Ghana Photovoltaic Inverter
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
