
Uninterruptible power supply systems provide protection
May 31, 2007 · This article describes the most common line problems and the relationship between these and the different existing kinds of UPS, showing their operation modes as well

UPS TO PROTECT POWER SUPPLY OF DATA CENTER
Apr 20, 2022 · INTRODUCTION The protection of Data Centers through static uninterruptible power supplies is essential to ensure continuity of the power supply and prevent damage

Uninterruptible Power Supply System
Aug 3, 2022 · Businesses today invest large sums of money in their IT infrastructure, as well as the power required to keep it functioning. Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) are an

How does AC & DC Current Work within a UPS?
Feb 5, 2020 · UPS rectifiers are resistant to electricity spikes and surges so don''t have to engage the batteries unnecessarily. The inverter converts the DC to

Comparison of the AC UPS
Dec 20, 2007 · Abstract—The paper presents a conceptual comparison of the inherent properties of the DC UPS and the AC UPS system solutions for uninterruptible operation of data centers

UPS Glossary, Uninterruptible Power Supply Definition
Welcome to our comprehensive UPS Technical Glossary, a resource for understanding key terms, acronyms, and concepts related to Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems. Whether

Uninterruptible Power Supply Circuit: A Reliable Solution for
This is where the Uninterruptible Power Supply Circuit (UPS circuit) comes into play. This guide provides a comprehensive look at the Uninterruptible Power Supply Circuit, covering

What Is a UPS and How Does It Work?
Dec 23, 2024 · A UPS, or uninterruptible power supply, is a device that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source fails. This is typically used to protect computers,
An overview of Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems
Apr 12, 2023 · Typically, static power electronics such as fast-switching high-current insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) are used to convert power. This article discusses the most

(PDF) Analysis of Uninterruptable Power Supply Critical-to
Jun 27, 2023 · The study maps the relationship between parameters such as temperature at the battery positive terminal, supply voltage, supply current, average power, and total energy

Analysis of the uninterruptible power supply influences to the power
May 24, 2019 · Abstract: Systems of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) are indispensable part of many industrial plants, transportation, telecommunications and other systems, enabling their

Uninterruptible Power Supplies
Jan 1, 2024 · Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems are used to provide uninterrupted, reliable, and high-quality power for these sensitive loads. Applications of UPS systems include
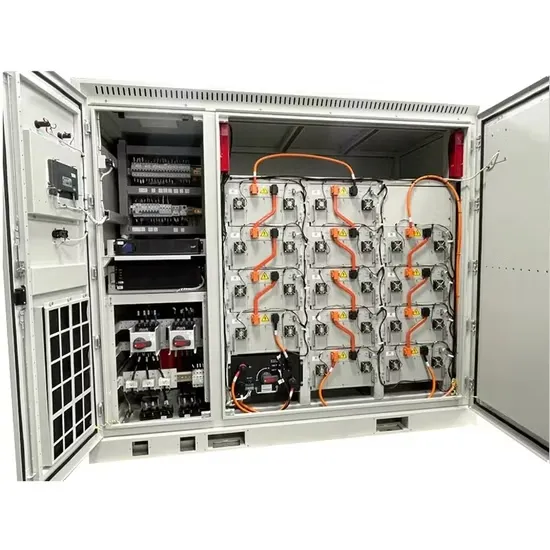

Overview of Uninterruptive Power Systems (UPS)
Sep 27, 2020 · An uninterruptible power supply is a device that has the ability to convert and control direct current (DC) energy to alternating current (AC) energy [1]. UPS is a battery

Analysis of uninterruptable power supply critical-to-quality
Jun 27, 2023 · The demand for a reliable power supply and electricity continues to increase, which has led to an increase in the production capacities of power generation units and regular

The difference between the voltage regulator and the UPS
Aug 9, 2018 · The functions are different, the voltage regulator and the UPS uninterruptible power supply are widely used, but there is a difference between the regulator and the UPS power

What is an uninterruptible power supply (UPS)? | Control
Nov 4, 2024 · An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is a device that provides backup power to critical systems in the event of a power failure. Unlike a generator, which can take time to start,

The Environmental Impact of UPS Systems: How to Choose
How do Uninterruptible Power Supply systems impact the environment? Uninterruptible Power Supply systems consume electricity, and the energy they use has an environmental impact.

Uninterruptible power supply systems provide protection
May 31, 2007 · Nowadays, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems are in use throughout the world, helping to supply a wide variety of critical loads, in situations of power outage or

Difference Between Standby Power Supply and Uninterruptible Power
Difference Between Standby Power Supply and Uninterruptible Power Supply In today''s technology-driven world, ensuring a reliable power supply is essential. Power interruptions can

Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) – Definition, Block
Dec 16, 2022 · Learn about Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), its definition, block diagram, types, and various applications in this comprehensive guide.

The difference between a UPS and an Inverter?
An uninterruptible power supply is a device that serves as a conduit between a mains power supply and a critical load. It has two functions, the first is to provide a backup power supply

AC Backup Power Using A Simulated Sine Wave
Feb 3, 2013 · A customer today requested an AC-output Uninterruptible Power Source (UPS) for our indoor Optical Network Termination (ONT) products. Product Management asked us to

6 FAQs about [The relationship between uninterruptible power supply and AC screen]
What is an uninterruptible power supply?
An uninterruptible power supply is a device that has the ability to convert and control direct current (DC) energy to alternating current (AC) energy . UPS is a battery backup for PC, when the power goes off the UPS kicks in and continues to supply power for some period of time to the particular system.
What is an AC ups & how does it work?
In an AC UPS, the incoming AC power is typically rectified to DC to charge a battery or a bank of batteries. During a power outage or disturbance, the stored DC power is then inverted back into AC power to provide a continuous and uninterrupted power supply to connected devices.
What is a static uninterruptible power supply (sups)?
The static uninterruptible power supply (SUPS) basically consists of four major blocks. They are the battery rectifier/charger, battery bank, inverter and the transfer switch. The rectifier/charger receives the normal alternating current (AC) power supply, provides direct current (DC) power to the inverter, and charges the battery.
What is the difference between AC & DC UPS?
The primary difference between AC UPS and DC UPS lies in the type of electrical current they use and the way they handle power during normal operation and outages. Here are the key distinctions between the two: Type of Power Input AC UPS: Accepts and uses AC as the input power source.
What is an uninterrupted power supply (UPS) system?
Abstract. In the modern world, when there is a power outage or a power failure, telecommunication systems, computer systems, and many other critical equipment, such as medical equipment, require uninterrupted power to support their operation. Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems are used for this purpose.
What are AC and DC currents in an UPS system?
Before we get onto the finer details regarding UPS systems, let’s quickly recap what AC and DC currents are. DC stands for direct current.The electrons travel in a single direction like a river or stream and flow constantly. DC power is used in batteries and electronic equipment such as TVs, computers, radios and mobile phones.
Update Information
- Qatar AC Uninterruptible Power Supply BESS
- Paramaribo AC Uninterruptible Power Supply
- Guinea AC UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply Company
- Converting AC to DC in an uninterruptible power supply
- Uninterruptible Power Supply Production in Bandar Seri Begawan
- Ups uninterruptible power supply backup battery
- Advantages of Distributed Uninterruptible Power Supply
- Tbb Uninterruptible Power Supply
- BESS Uninterruptible Power Supply in Osaka Japan
- How much does Indonesian uninterruptible power supply BESS cost
- Nicosia single phase uninterruptible power supply manufacturer
- UK UPS uninterruptible power supply manufacturer
- Uninterruptible power supply capacity
Solar Storage Container Market Growth
The global solar storage container market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 200% in the past two years. Pre-fabricated containerized solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new utility-scale storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 40% market share, driven by streamlined permitting processes and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 15-25%. Europe follows closely with 32% market share, where standardized container designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with China's manufacturing scale reducing container prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting mobile container solutions for rapid electrification, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Major projects now deploy clusters of 20+ containers creating storage farms with 100+MWh capacity at costs below $280/kWh.
Containerized System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar storage container performance while reducing costs. Next-generation thermal management systems maintain optimal operating temperatures with 40% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $80/kWh to $45/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple containers to operate as coordinated virtual power plants, increasing revenue potential by 25% through peak shaving and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and gas detection systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for container-based projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple container additions at just $210/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show 20ft containers (1-2MWh) starting at $350,000 and 40ft containers (3-6MWh) from $650,000, with volume discounts available for large orders.
